ZYNRELEF was generally well tolerated in clinical trials
- The safety of ZYNRELEF has now been evaluated in a total of 1,627 patients undergoing various surgical procedures across 14 clinical studies, including 7 randomized, double-blind, bupivacaine- and placebo-controlled and saline placebo–controlled studies designed to investigate ZYNRELEF1-5
- ZYNRELEF had a similar safety profile to that of placebo and bupivacaine HCl solution1-4
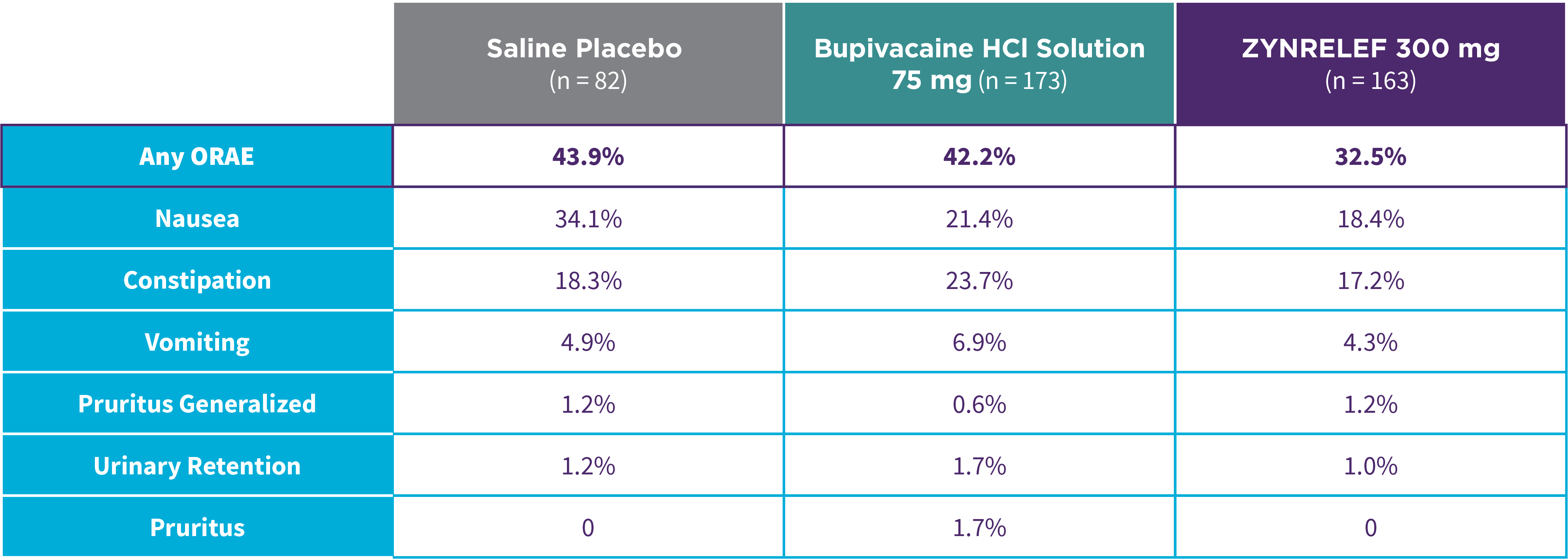
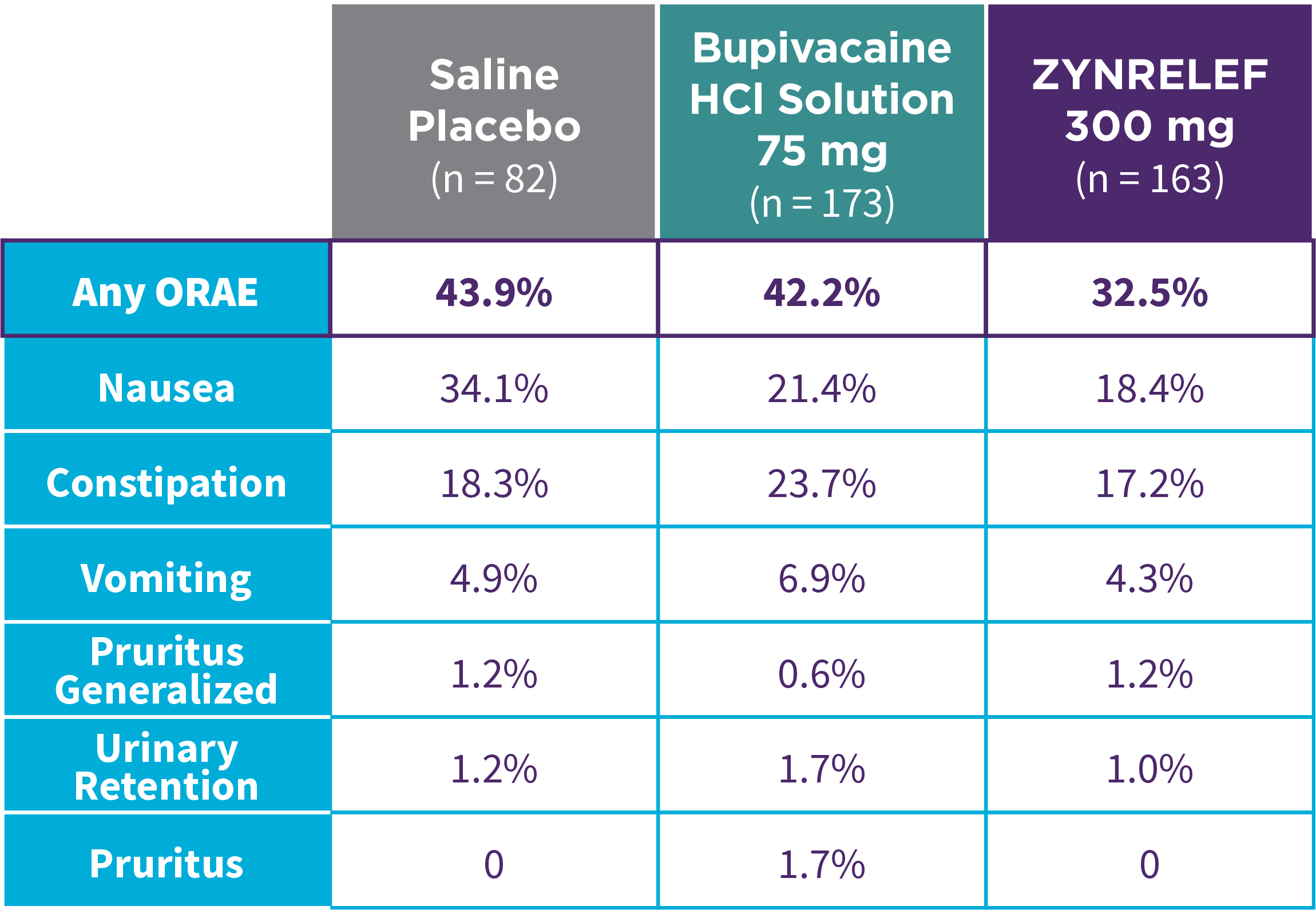
- Patients treated with ZYNRELEF experienced a lower overall incidence of opioid-related adverse events compared to saline placebo and bupivacaine HCl solution2,3
- ZYNRELEF was well tolerated when used concomitantly with aspirin, ropivacaine, and acetaminophen4,6-8
- In patients receiving ketorolac, celecoxib, or ibuprofen in addition to ZYNRELEF, no increase in NSAID-related toxicity was seen6,7,9,10
Following administration of ZYNRELEF, if additional NSAID medication is indicated in the postoperative period, monitor patients for signs and symptoms of NSAID-related GI adverse reactions.
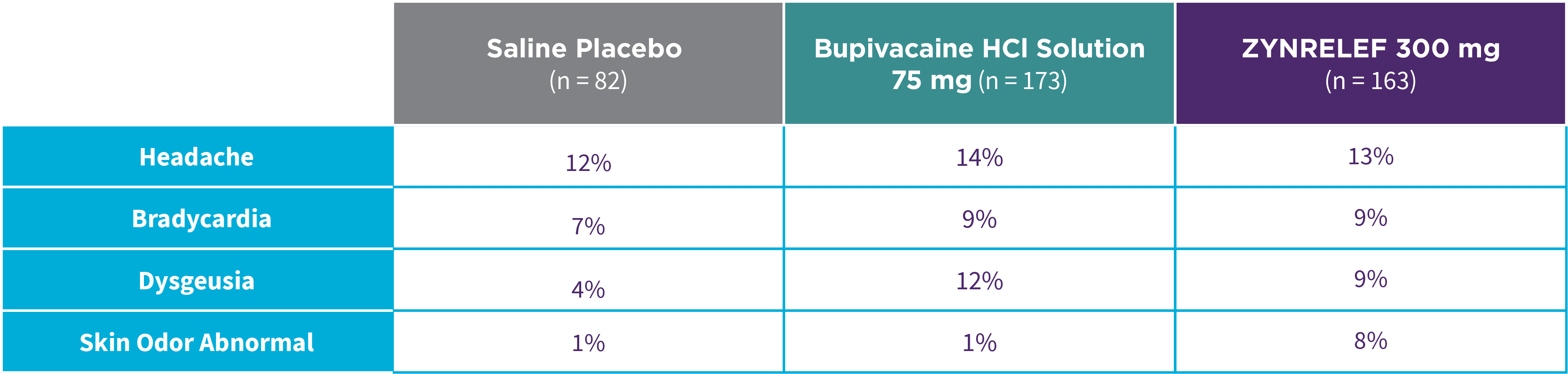
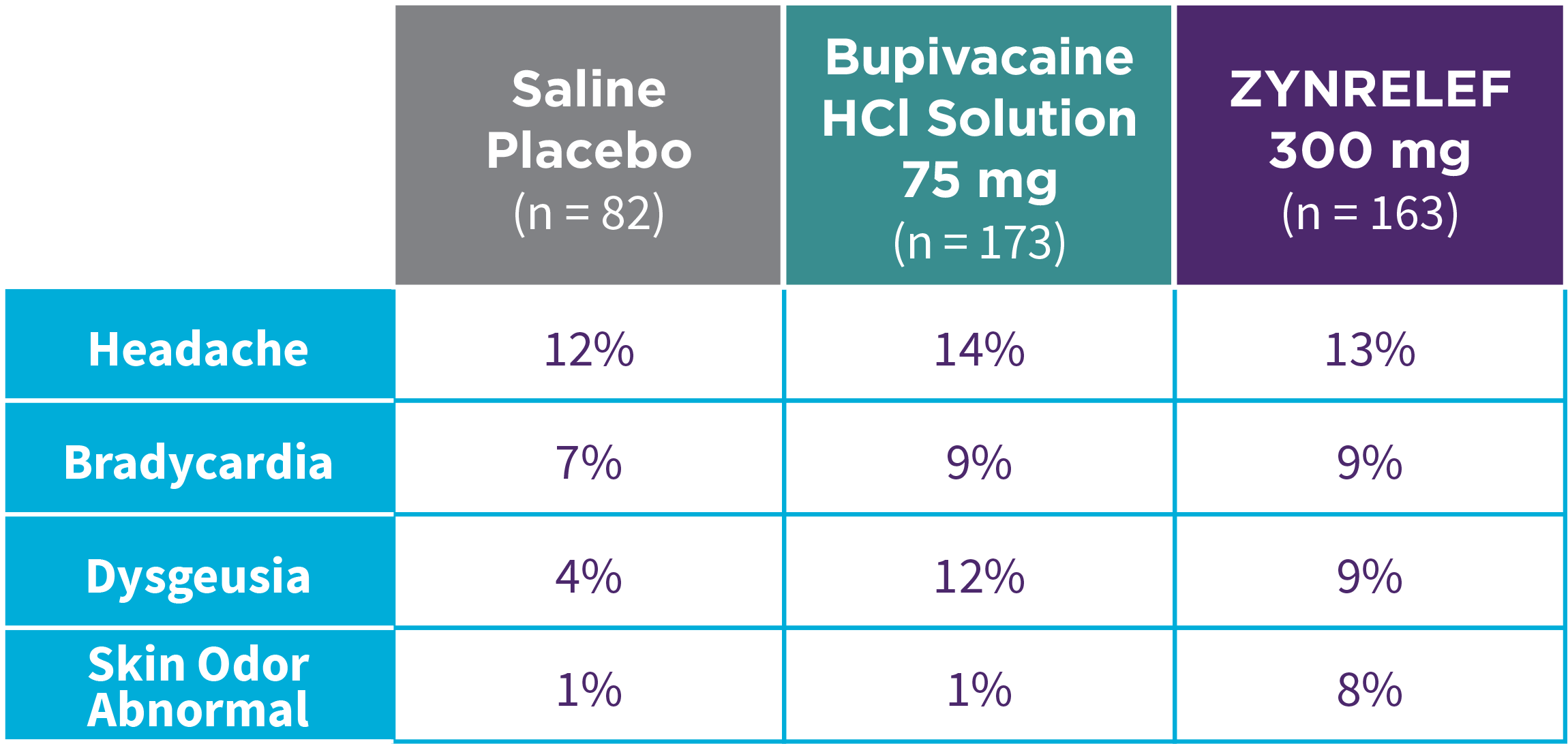
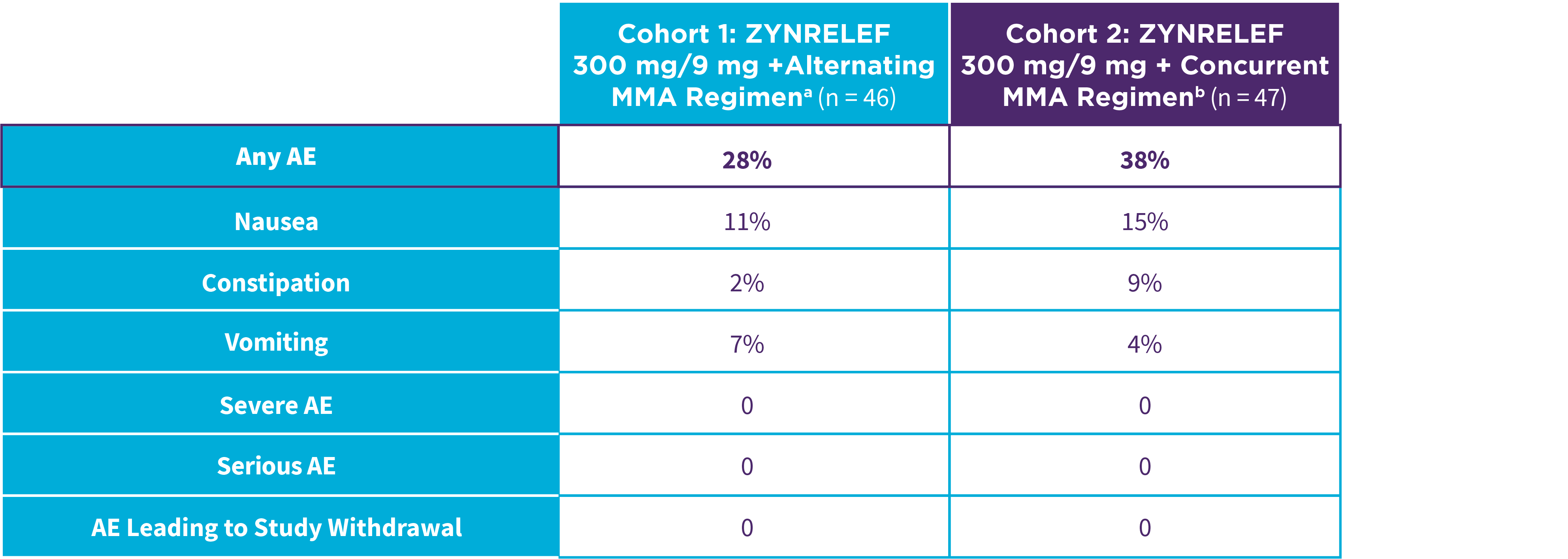
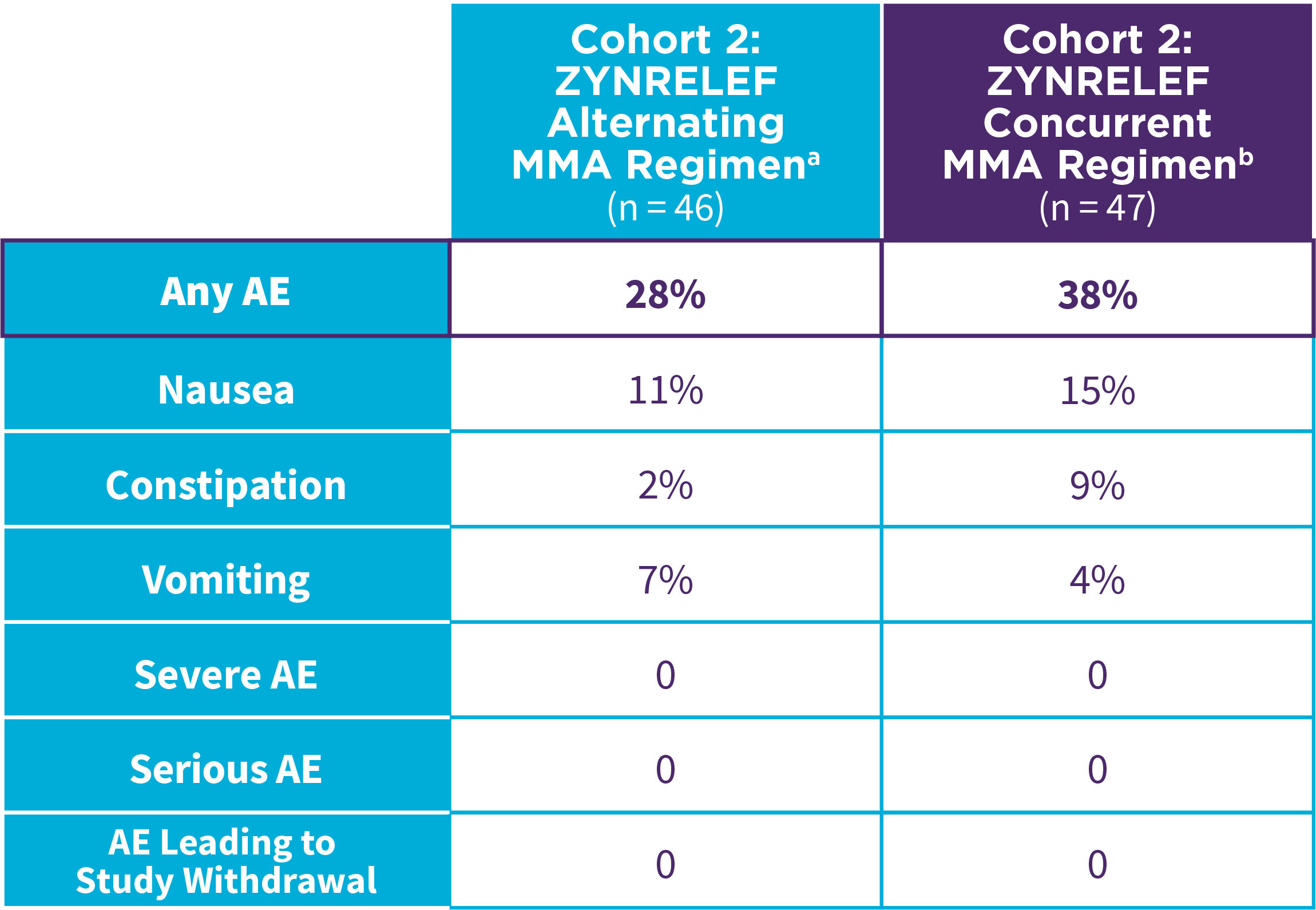
Bunionectomy
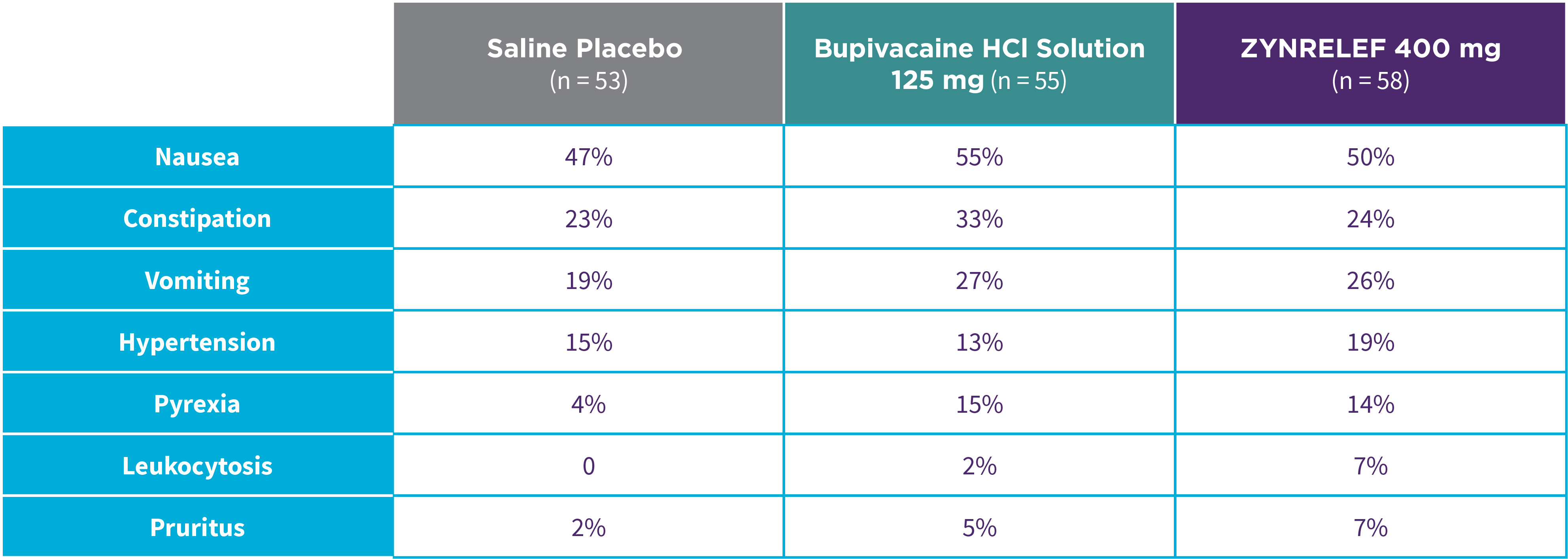
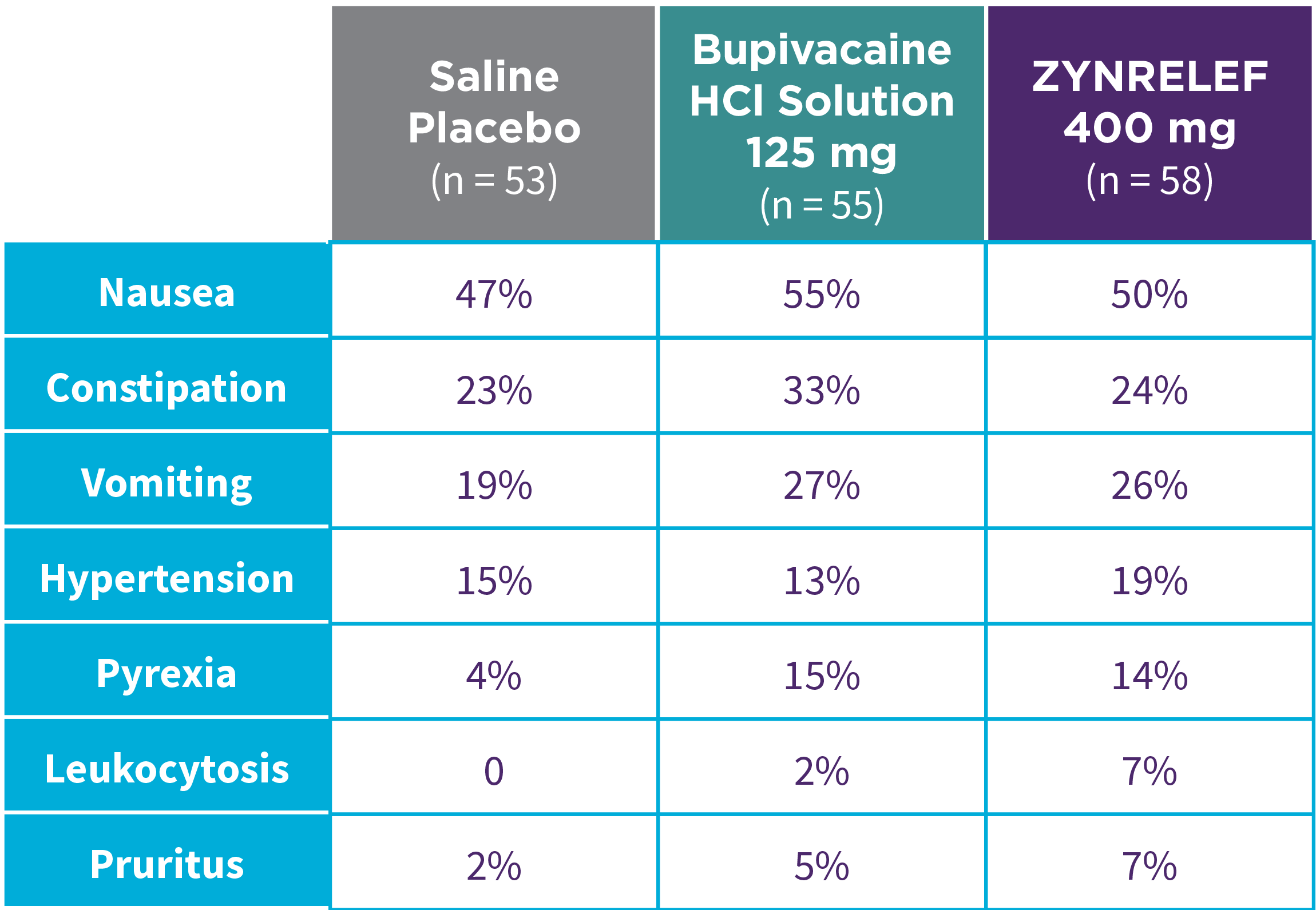
EPOCH 1 Bunionectomy: Incidence of adverse reactions1,2,11
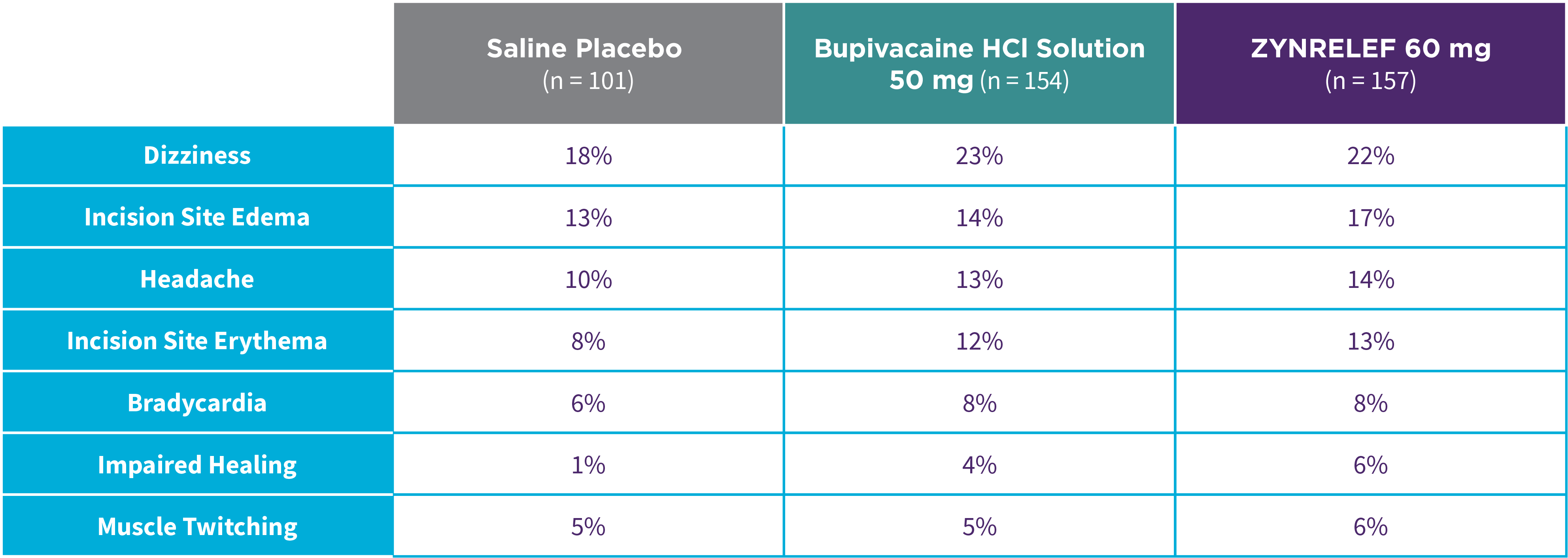
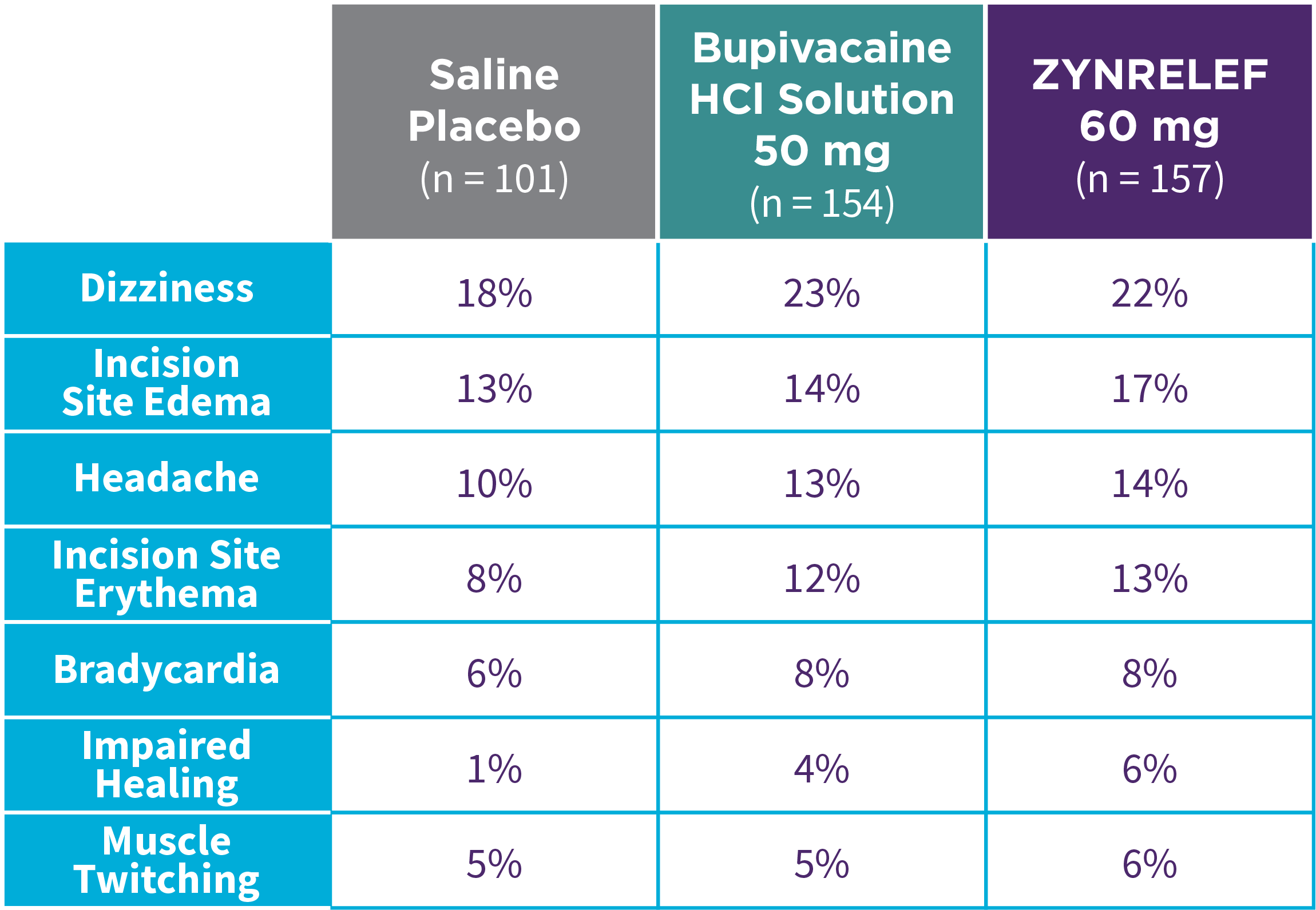
Note: Events included are adverse reactions with an incidence of ≥5% in the ZYNRELEF group.
Local inflammatory adverse events occurring in ≥2% of patients treated with ZYNRELEF with a higher incidence than with saline placebo included incision site cellulitis (4% incidence with ZYNRELEF, compared to 1% with both bupivacaine HCl solution and saline placebo); wound dehiscence (4% with ZYNRELEF, compared to 1% with bupivacaine HCl solution and 2% with saline placebo); and incision site infection (3% with ZYNRELEF, compared to 1% with bupivacaine HCl solution and 0% with saline placebo). In EPOCH 1 Bunionectomy, bone healing was assessed by X-ray on days 28 and 42. There was no difference in bone healing between treatment groups. A total of 4 subjects had delayed bone healing: 1 in the ZYNRELEF group, 1 in the saline placebo group, and 2 in the bupivacaine HCl group.
EPOCH 1 Bunionectomy: Lower overall incidence of opioid-related adverse events2,11
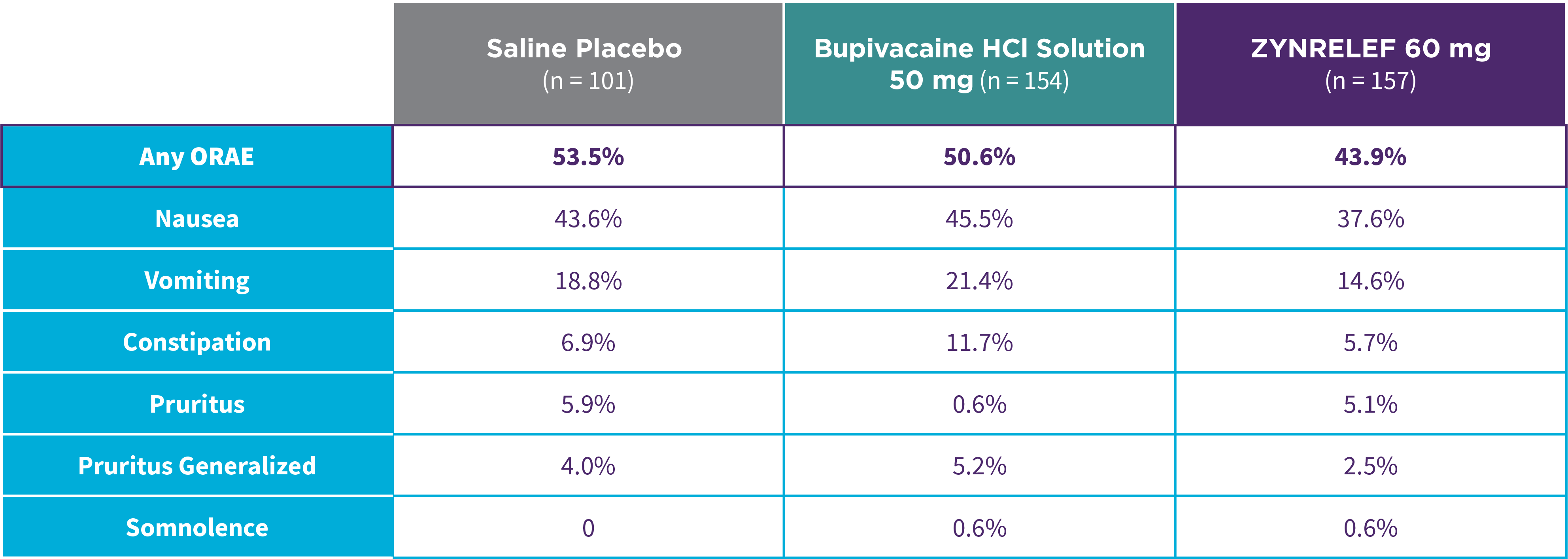
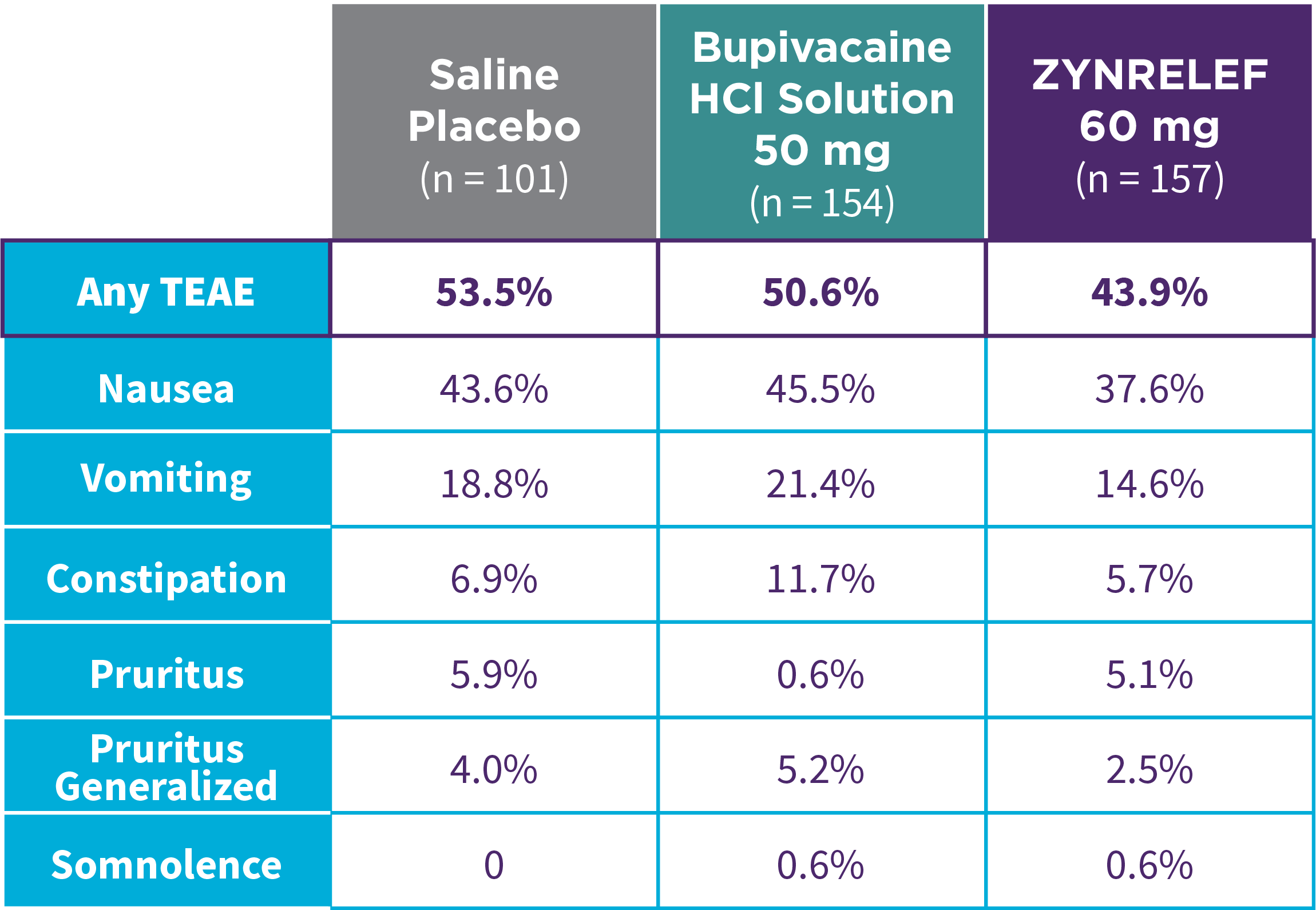
Note: ORAEs were defined as nausea, vomiting, constipation, pruritus, pruritus generalized, somnolence, respiratory depression, and urinary retention. These adverse events were considered ORAEs regardless of whether a patient received opioids.
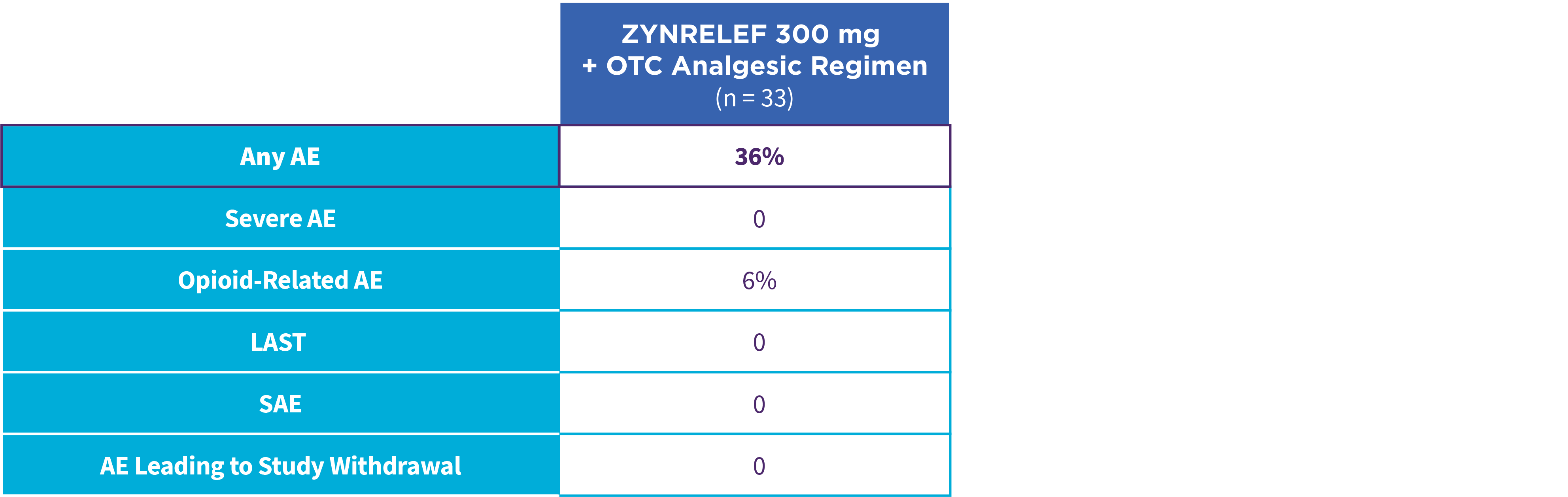
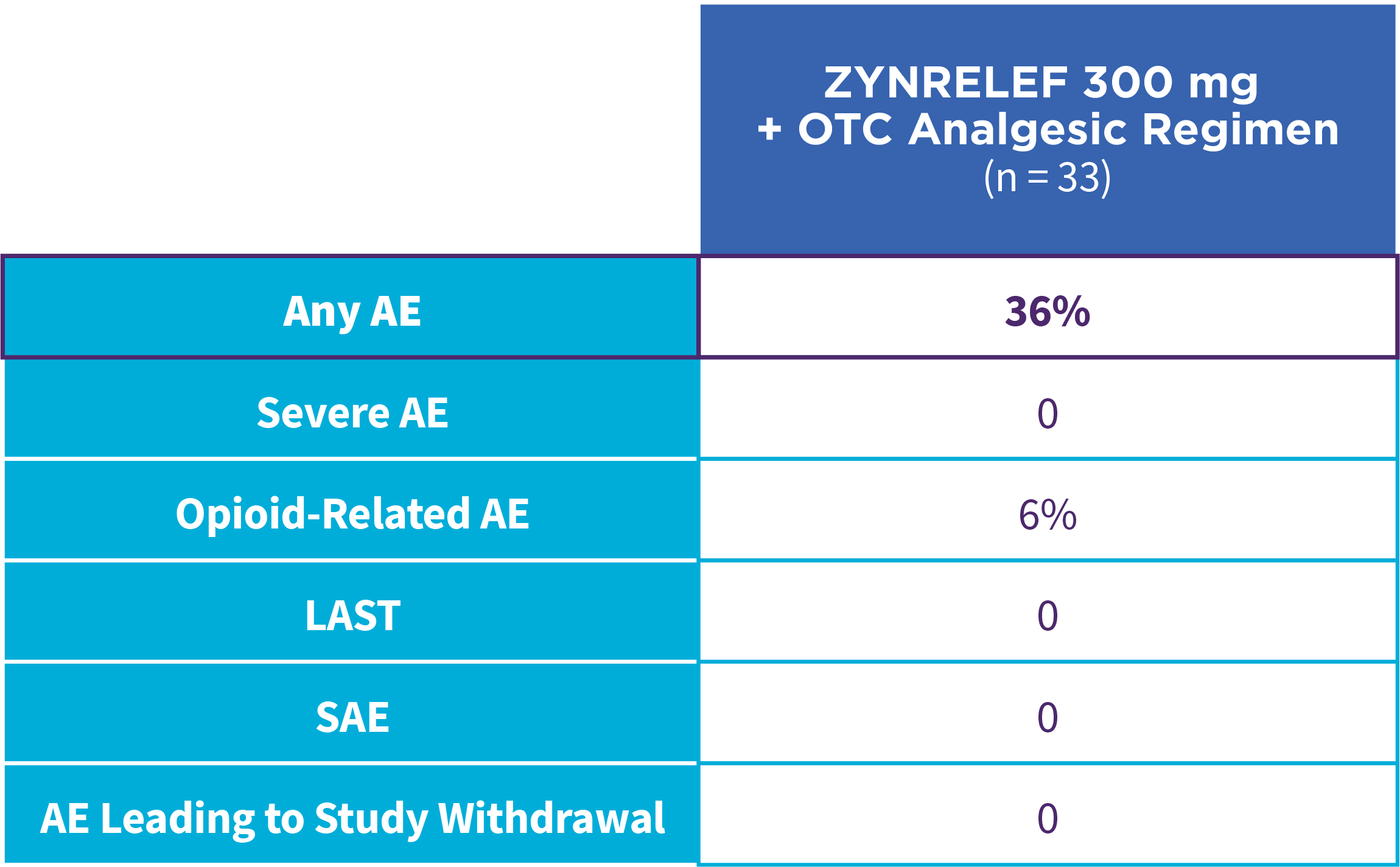
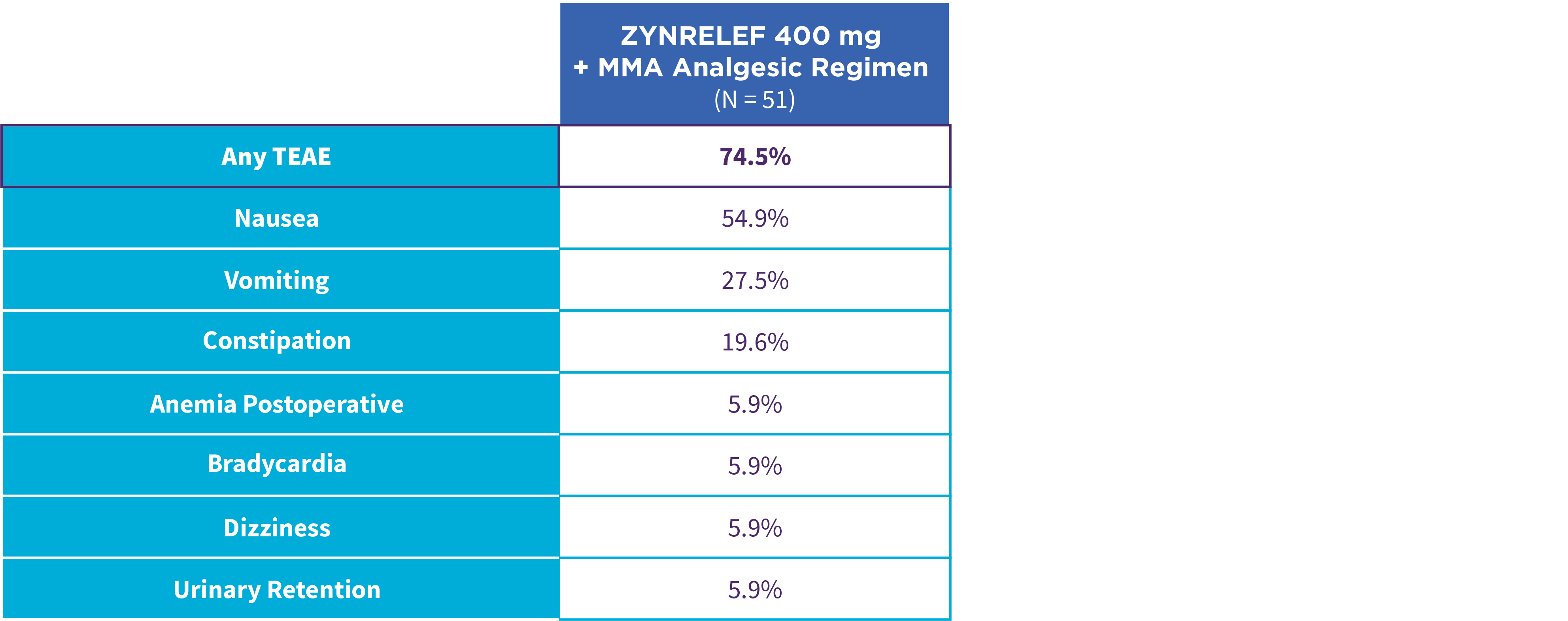
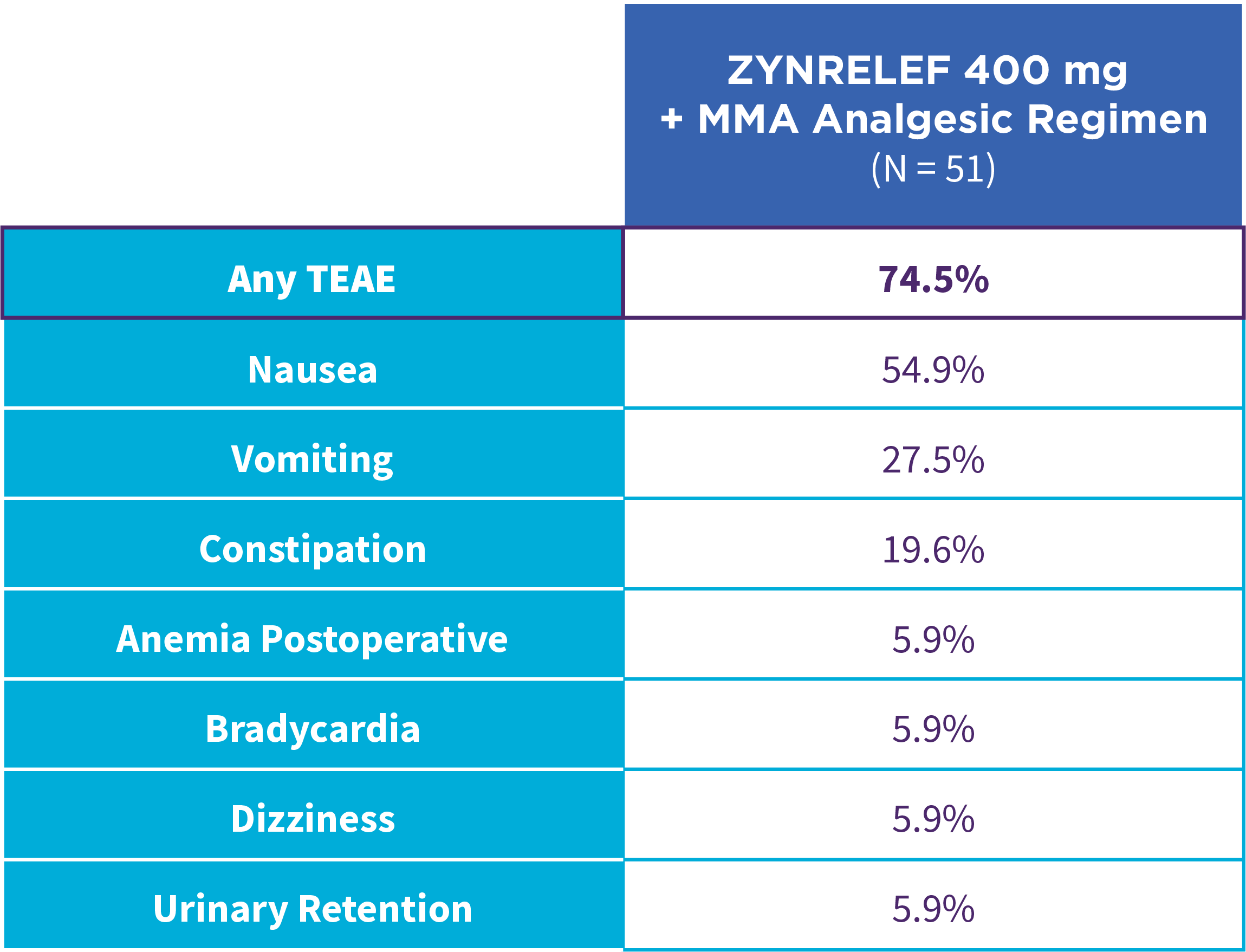
EPOCH 1 Single-Arma Follow-On: Incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events7,12
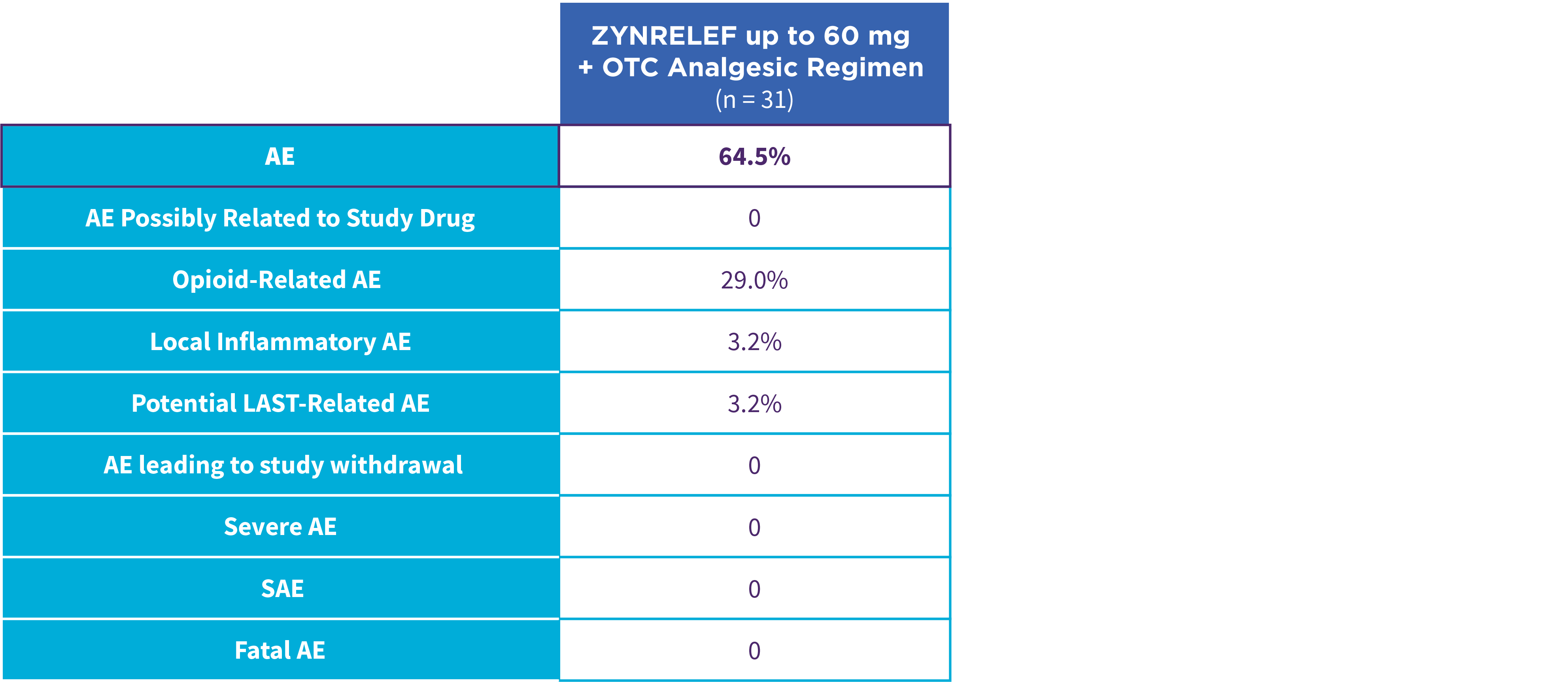
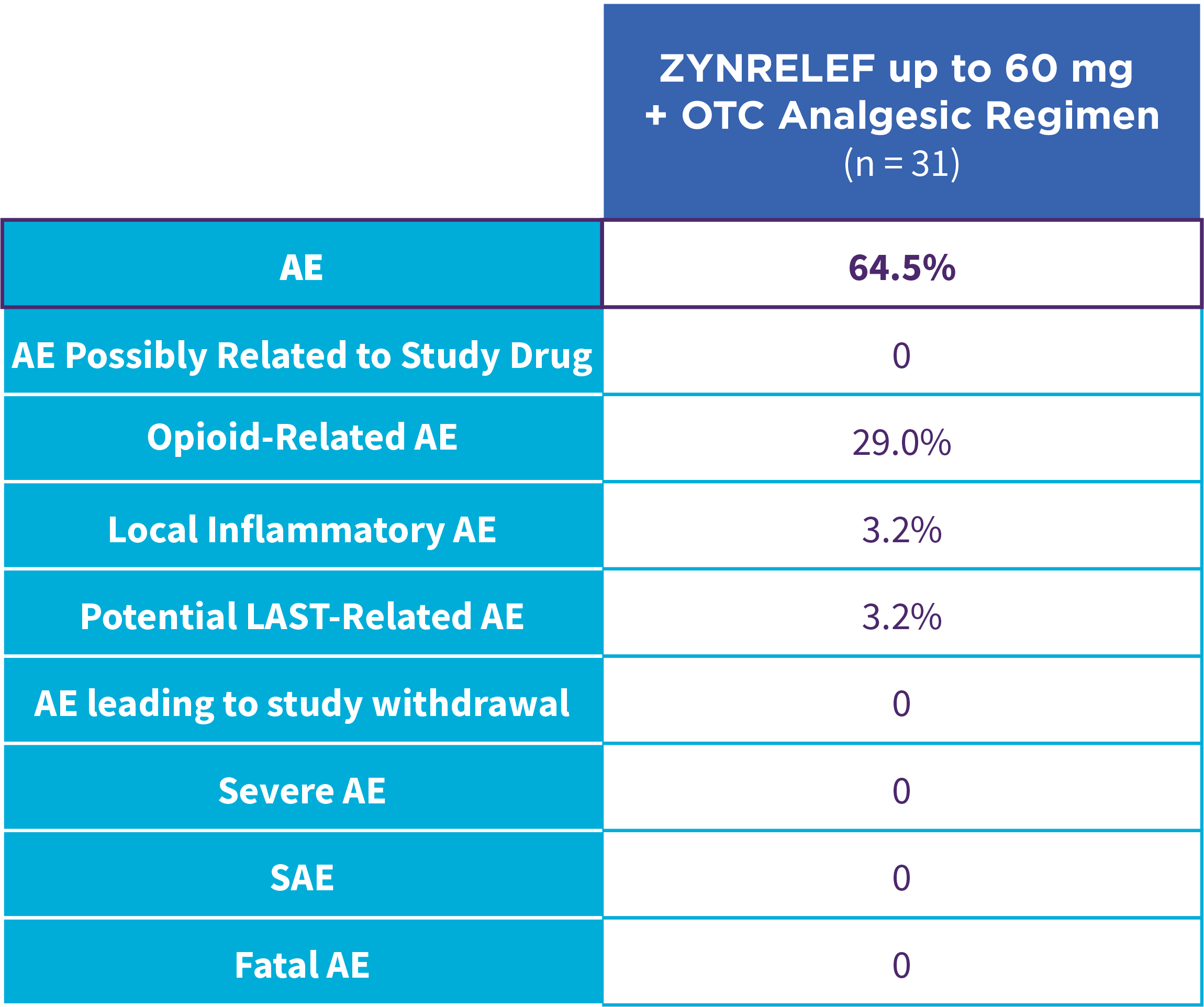
OTC: over-the-counter. AE: adverse event. LAST: local anesthetic systemic toxicity. Severe Adverse Event: any adverse event that interrupted daily activity or required systemic drug therapy or treatment. Serious Adverse Event: any adverse event that was life threatening, resulted in substantial disruption to normal life, caused a birth defect, or required medical intervention.
aSingle-arm, open-label, uncontrolled study. ZYNRELEF was given with a scheduled non-opioid MMA regimen.
Learn how ZYNRELEF can help in your practice
Important Safety Information and Indication
Indication
ZYNRELEF is indicated in adults for instillation to produce postsurgical analgesia for up to 72 hours after soft tissue and orthopedic procedures including foot and ankle, and other procedures in which direct exposure to articular cartilage is avoided.
Limitations of Use: Safety and efficacy have not been established in highly vascular surgeries, such as intrathoracic, large 4 or more level spinal, and head and neck procedures.
Important Safety Information
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use.
- ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events.
Contraindications
ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity (eg, anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to any amide local anesthetic, NSAIDs, or other components of ZYNRELEF; with history of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients); undergoing obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia; or undergoing CABG.
Warnings and Precautions
Dose-Related Toxicity: Monitor cardiovascular and respiratory vital signs and patient’s state of consciousness after application of ZYNRELEF. When using ZYNRELEF with other local anesthetics, overall local anesthetic exposure must be considered through 72 hours.
Hepatotoxicity: If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medication may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure.
Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of ZYNRELEF in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure.
Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of ZYNRELEF in patients with advanced renal disease unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal failure.
Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
Risk of Joint Cartilage Necrosis and Degeneration with Unapproved Intra-articular Use: Animal studies evaluating the effects of ZYNRELEF following intra-articular administration in the knee joint demonstrated cartilage necrosis and degeneration.
Chondrolysis: Limit exposure to articular cartilage due to the potential risk of chondrolysis.
Methemoglobinemia: Cases have been reported with local anesthetic use.
Serious Skin Reactions: NSAIDs, including meloxicam, can cause serious skin adverse reactions. NSAIDs can also cause fixed drug eruption (FDE). FDE may present as a more severe variant known as generalized bullous fixed drug eruption (GBFDE), which can be life-threatening. If symptoms present, evaluate clinically.
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): If symptoms are present, evaluate clinically.
Fetal Toxicity: Due to the risk of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction and premature closure of the ductus arteriosus with NSAIDs, limit use of ZYNRELEF between about 20 to 30 weeks gestation, and avoid use after about 30 weeks.
Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia.
Drug Interactions
Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis: Monitor patients for bleeding who are using ZYNRELEF with drugs that interfere with hemostasis (eg, warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs).
ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs), or Beta-Blockers: Use with ZYNRELEF may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure.
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Use with ZYNRELEF in elderly, volume-depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high-risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function.
Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects.
Use in Specific Populations
Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider avoidance of ZYNRELEF in women who have difficulties conceiving.
Severe Hepatic Impairment: Only use if benefits are expected to outweigh risks; monitor for signs of worsening liver function.
Severe Renal Impairment: Not recommended.
Adverse Reactions
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) in controlled clinical trials with ZYNRELEF are soft tissue procedures: vomiting and orthopedic procedures: constipation and headache.
Report side effects to Heron at 1-844-437-6611 or to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Indication
ZYNRELEF is indicated in adults for instillation to produce postsurgical analgesia for up to 72 hours after soft tissue and orthopedic procedures including foot and ankle, and other procedures in which direct exposure to articular cartilage is avoided.
Limitations of Use: Safety and efficacy have not been established in highly vascular surgeries, such as intrathoracic, large 4 or more level spinal, and head and neck procedures.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning and updated Warnings and Precautions for serious skin reactions caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Connect with Heron Therapeutics
How could you incorporate ZYNRELEF as the foundation of your institution’s postoperative pain management strategy? Connect with us to find out.
Fields marked with an asterisk (*) are required.
Thank you for your interest
In the meantime, you can learn more about ZYNRELEF by viewing our Frequently Asked Questions or downloading our Resources.
For general information:
844-HERON11 (844-437-6611)