Experience a world with fewer postoperative opioids
JUMP TO SECTION:
JUMP TO SECTION:
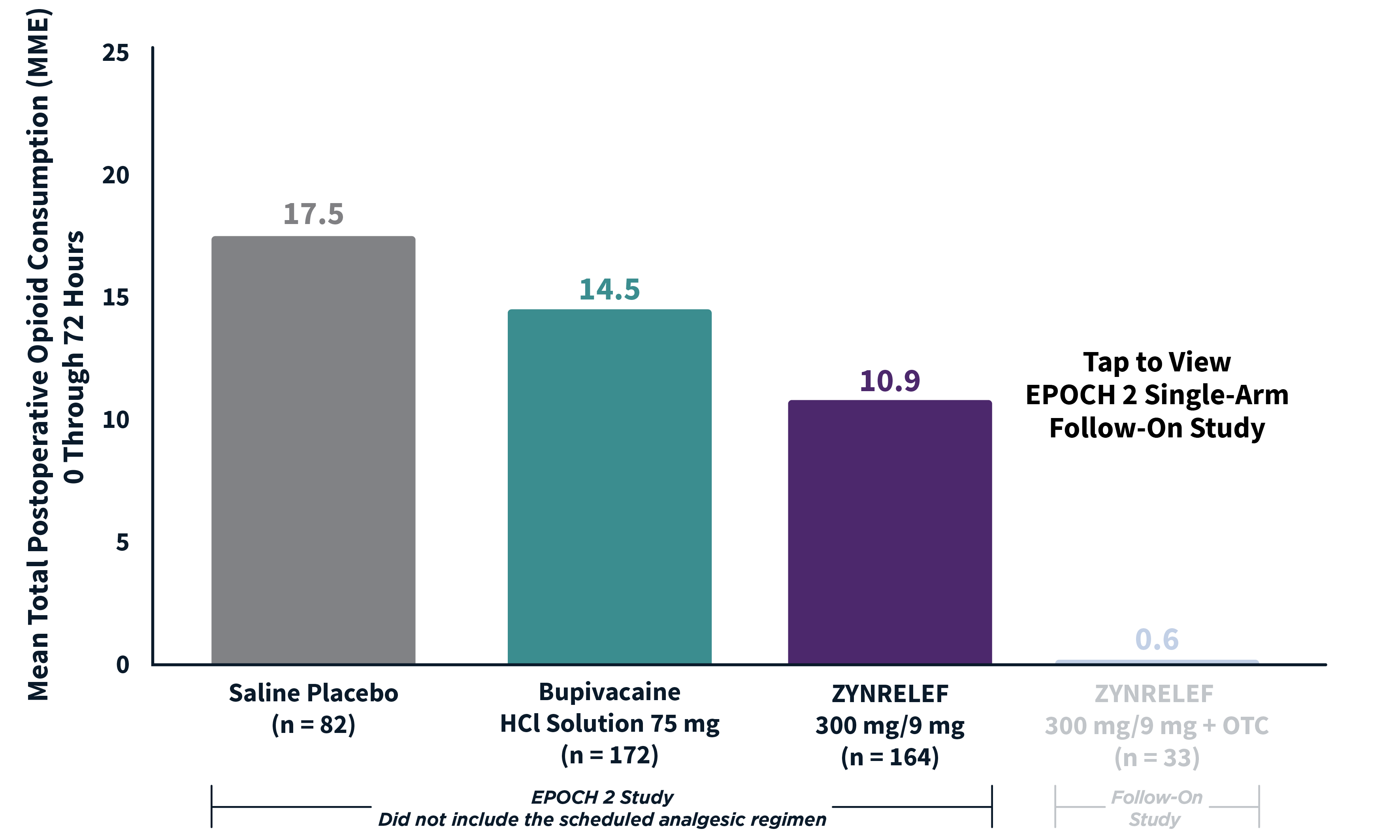
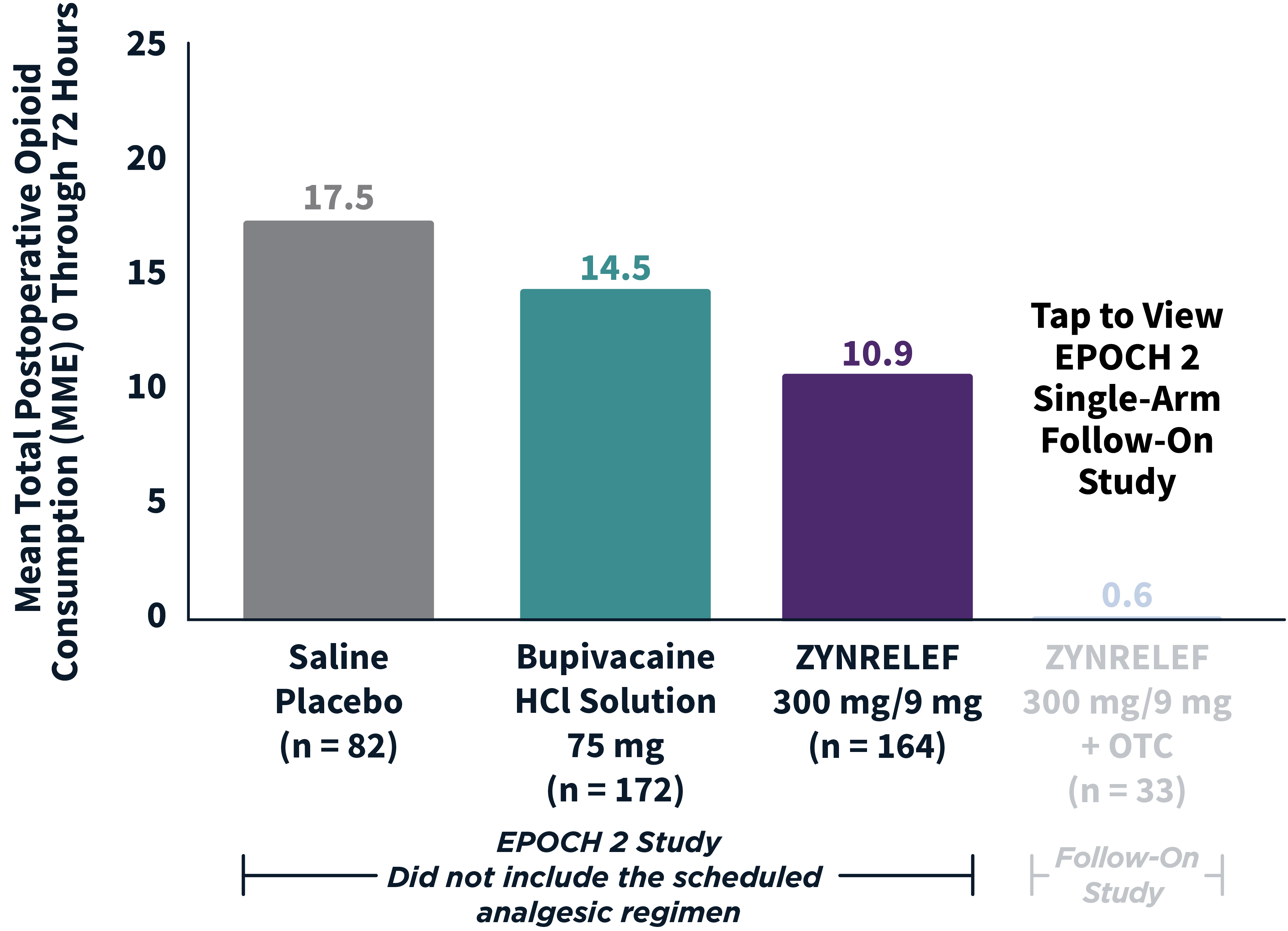
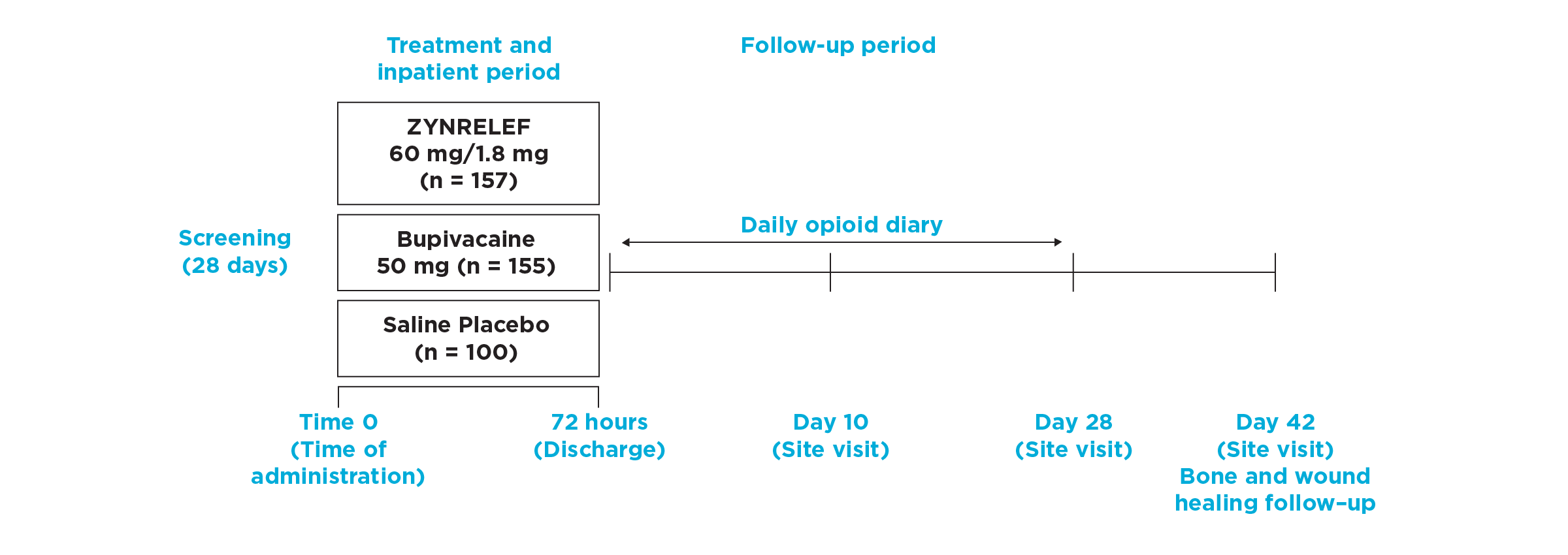
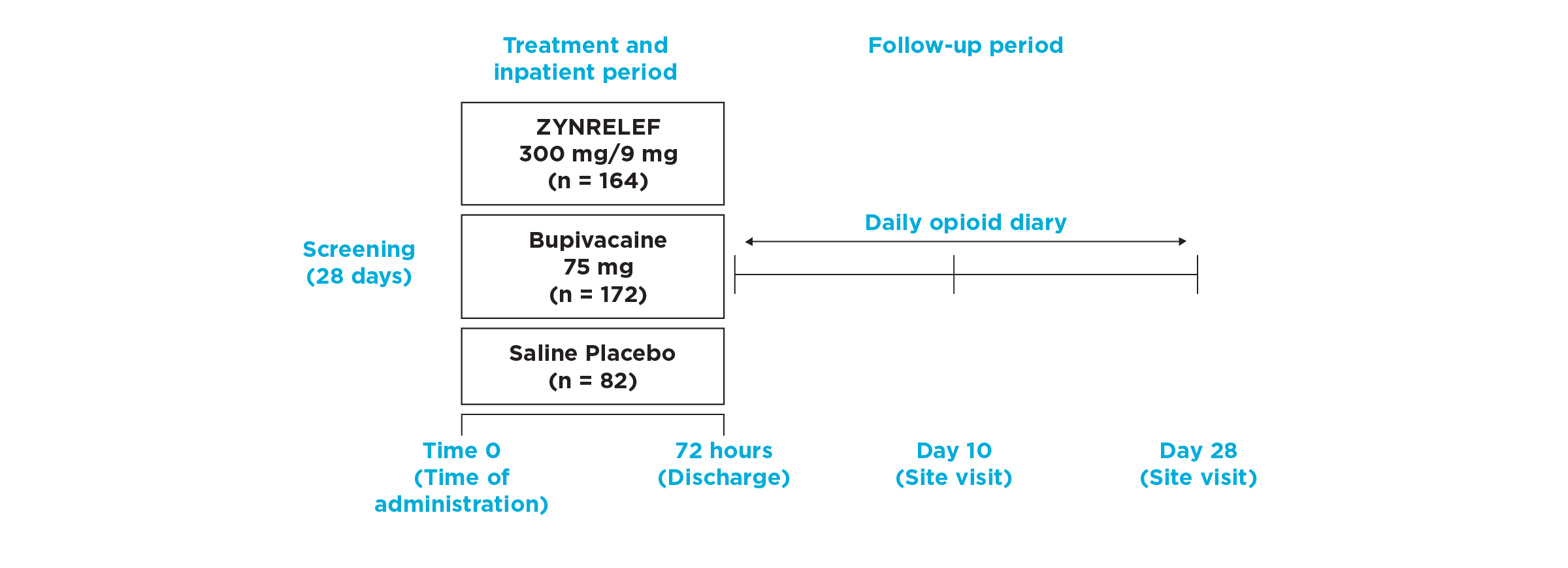
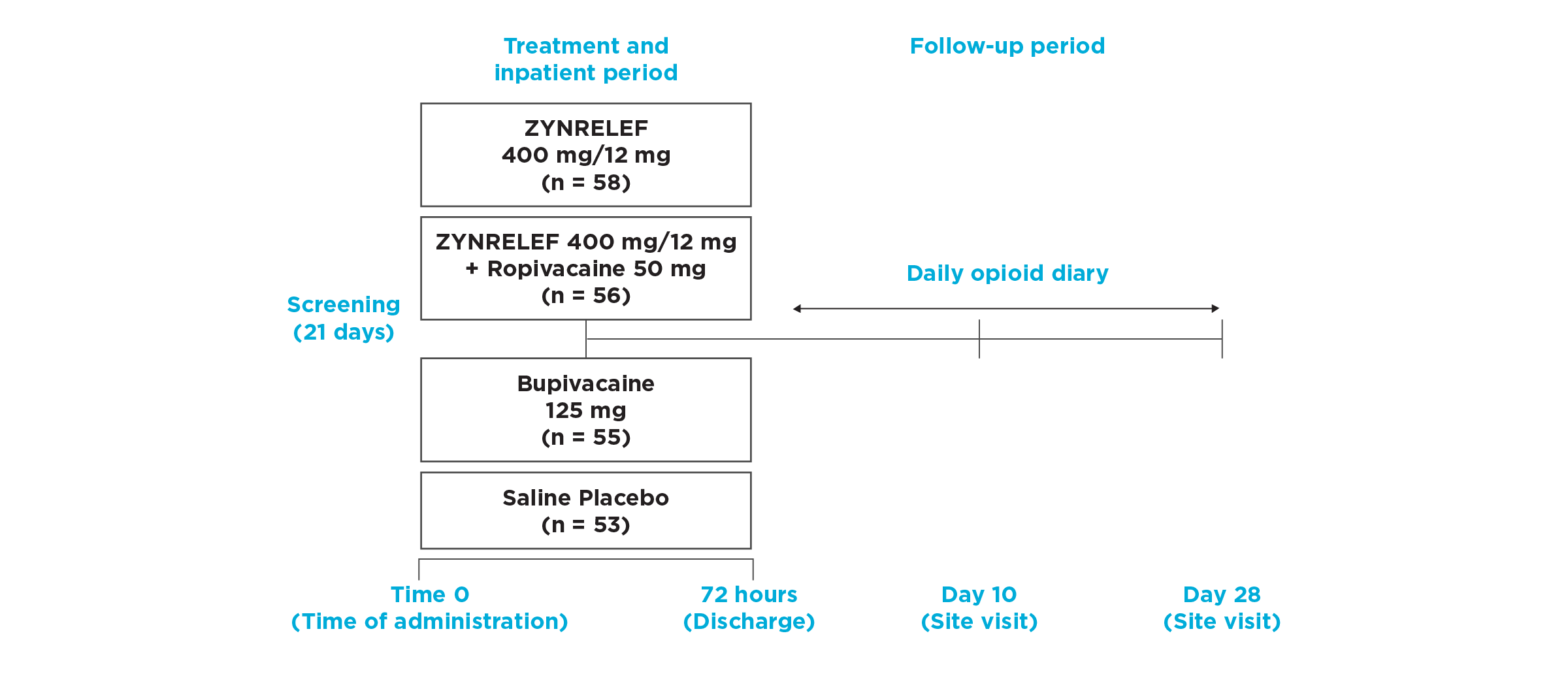
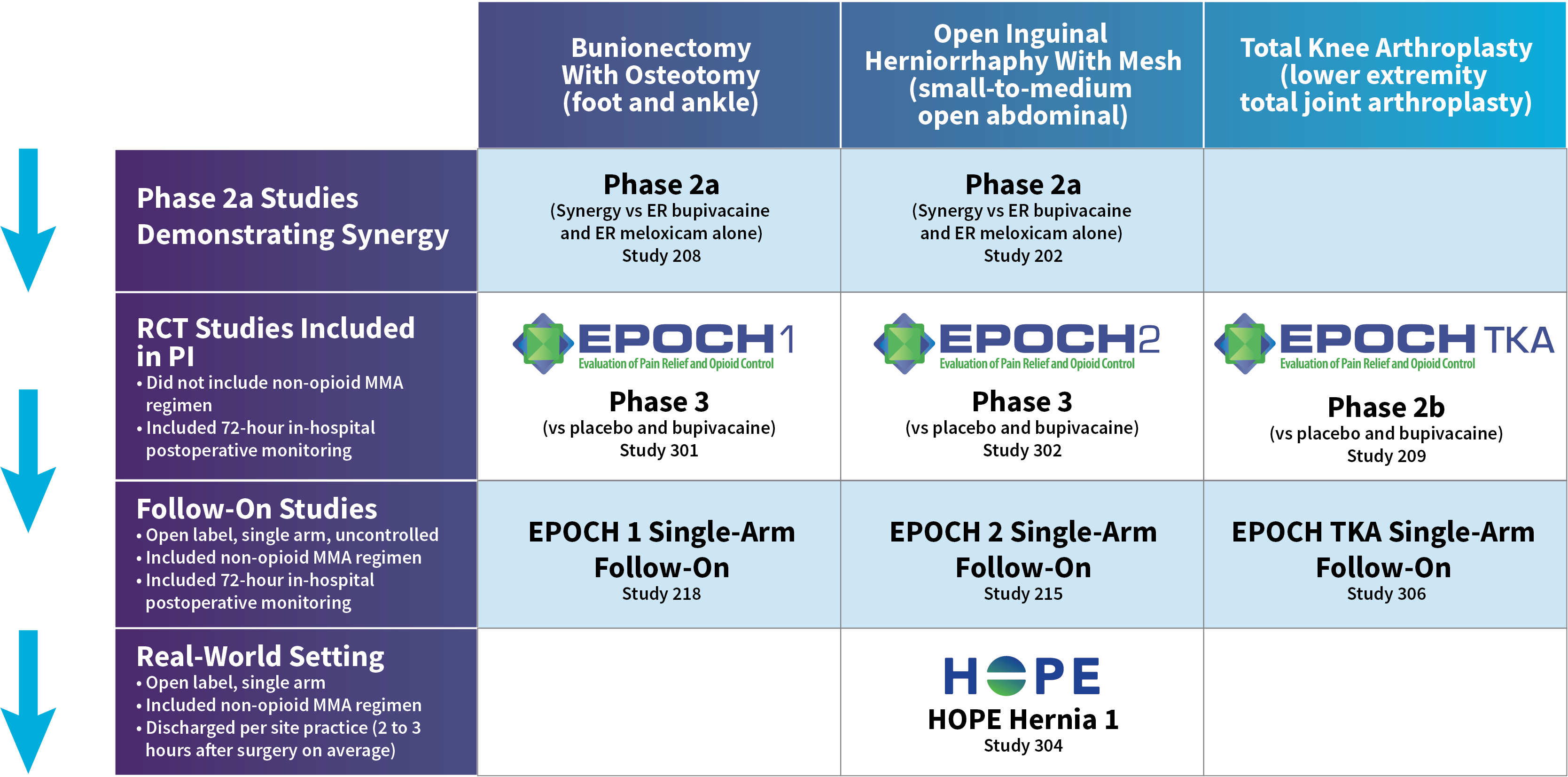
In EPOCH 1 Bunionectomy and EPOCH 2 Herniorrhaphy, patients treated with ZYNRELEF demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in opioid use compared to those treated with bupivacaine HCl solution and placebo, with significantly more patients requiring no opioids. In EPOCH TKA, patients treated with ZYNRELEF required fewer opioids than those treated with bupivacaine HCl solution or placebo.1-4
Based on the extrapolation of efficacy of ZYNRELEF across the 3 double-blind, controlled studies in patients undergoing bunionectomy, unilateral open inguinal herniorrhaphy, and total knee arthroplasty, and the pharmacokinetic profiles across surgical procedures with varied characteristics, such as anatomic location, tissue type, length and depth of surgical area, and vascularity, the pharmacokinetic profile and effectiveness of ZYNRELEF are not expected to be clinically significantly different when ZYNRELEF is administered at an appropriate dose in other soft tissue and orthopedic surgical procedures.1
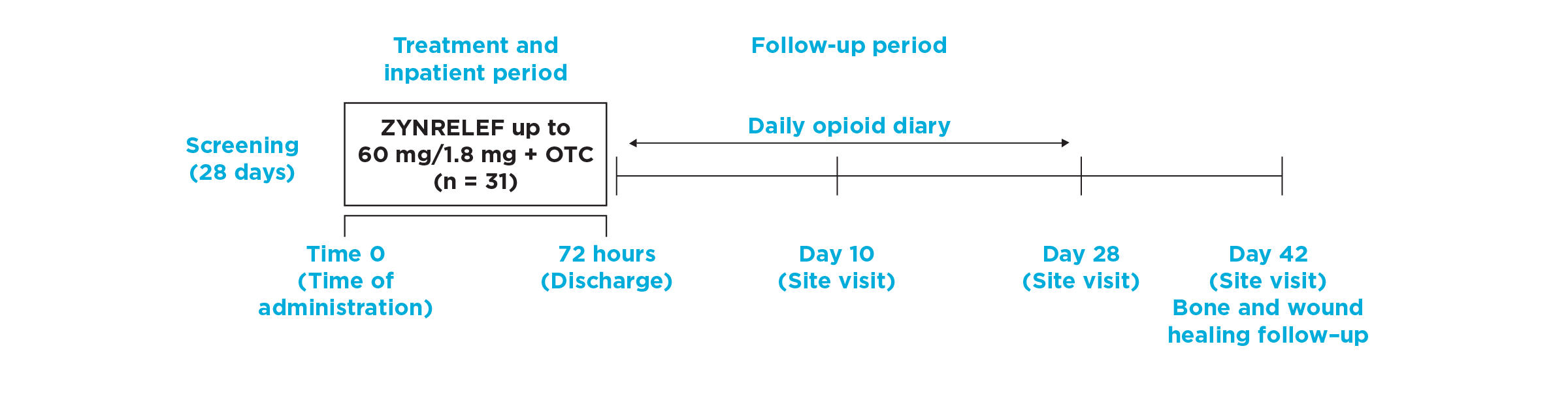
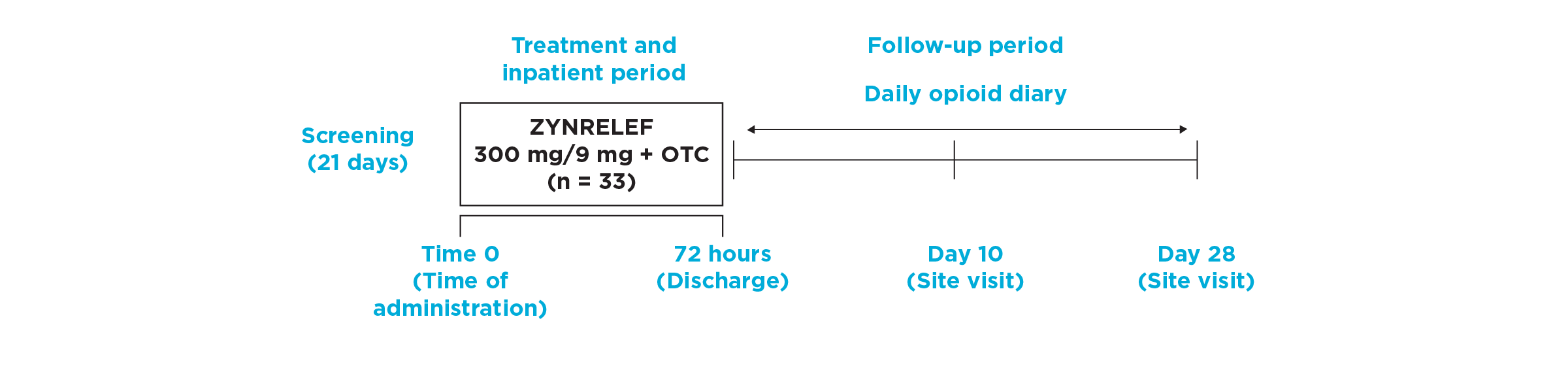
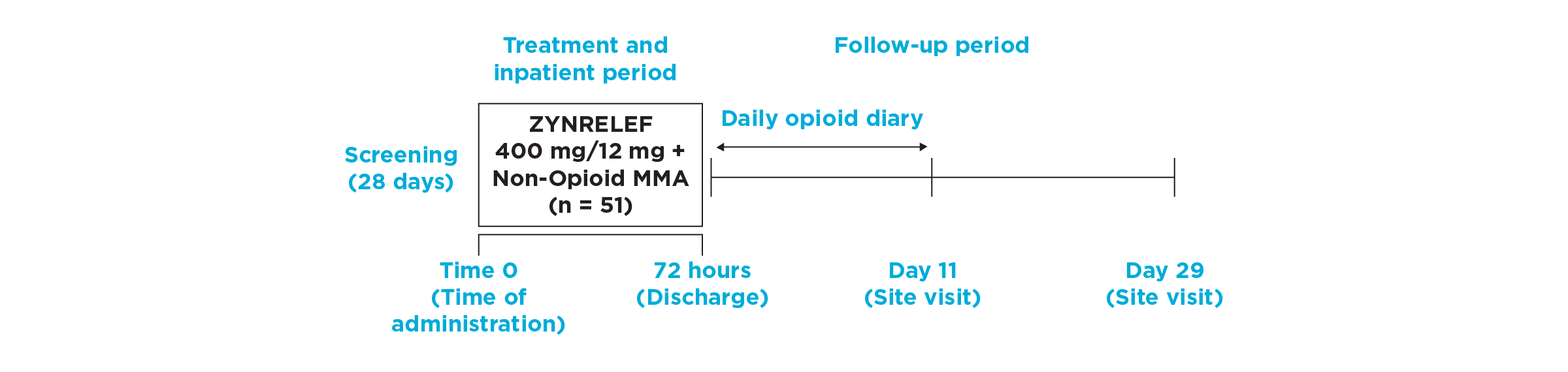
After the successful completion of the initial studies, ZYNRELEF was used as the foundation of a scheduled non-opioid multimodal regimen to further reduce patients’ need for opioids in EPOCH 1 Single-Arm Follow-On, EPOCH 2 Single-Arm Follow-On, and EPOCH TKA Single-Arm Follow-On. These follow-on studies were open-label, and were conducted without a control group as superiority to placebo and standard-of-care bupivacaine HCl solution had already been established in the initial studies.5-8
Following administration of ZYNRELEF, if additional NSAID medication is indicated in the postoperative period, monitor patients for signs and symptoms of NSAID-related GI adverse reactions.
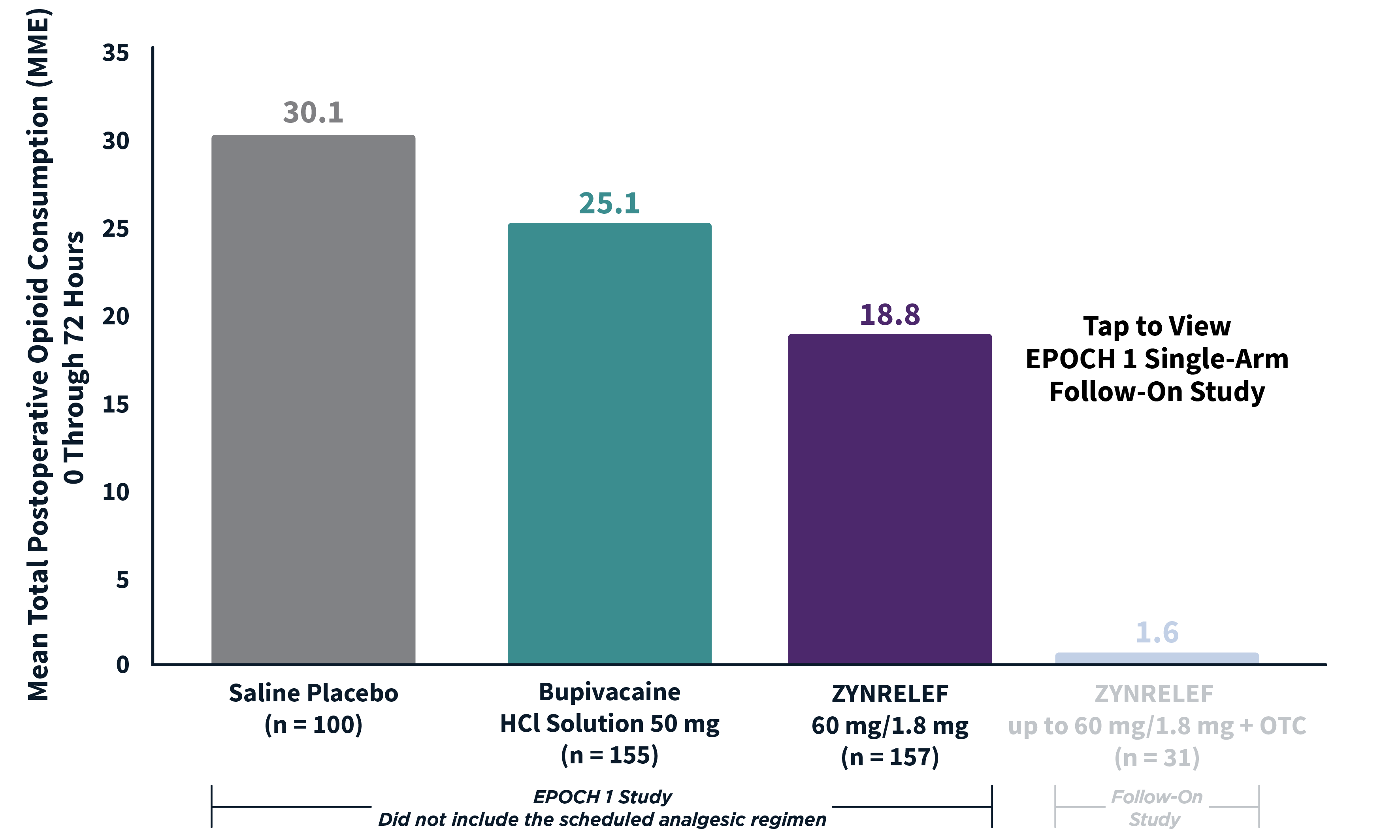
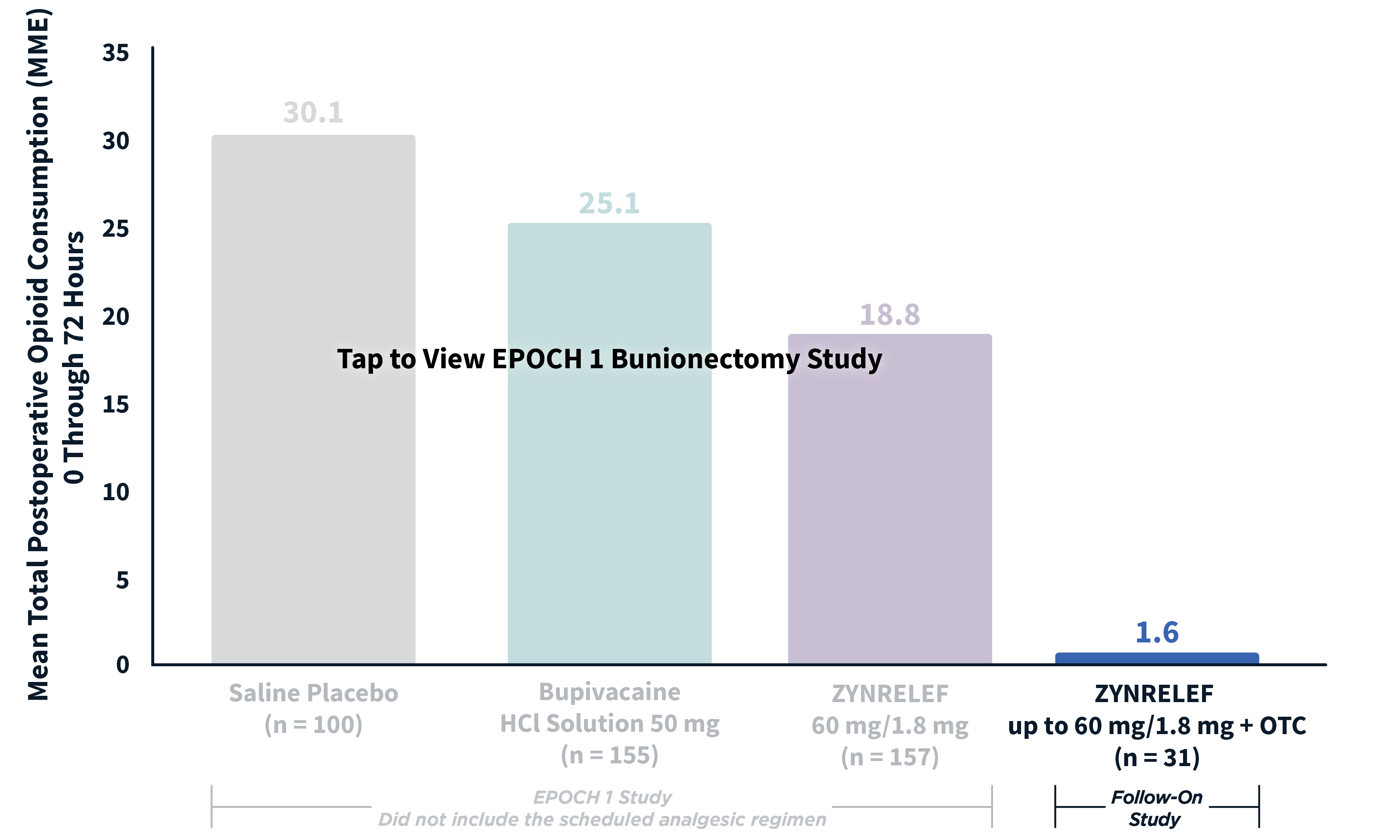
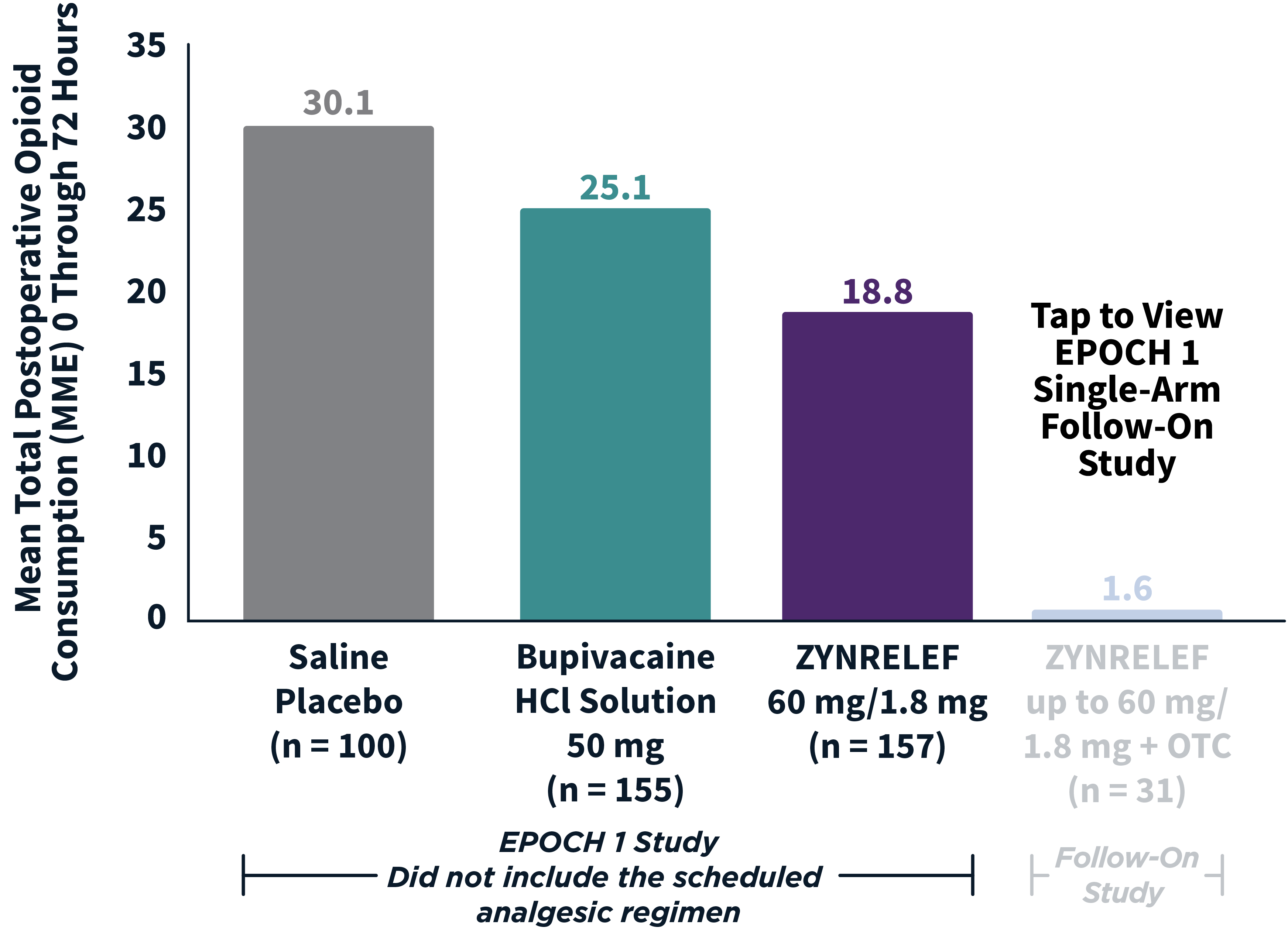
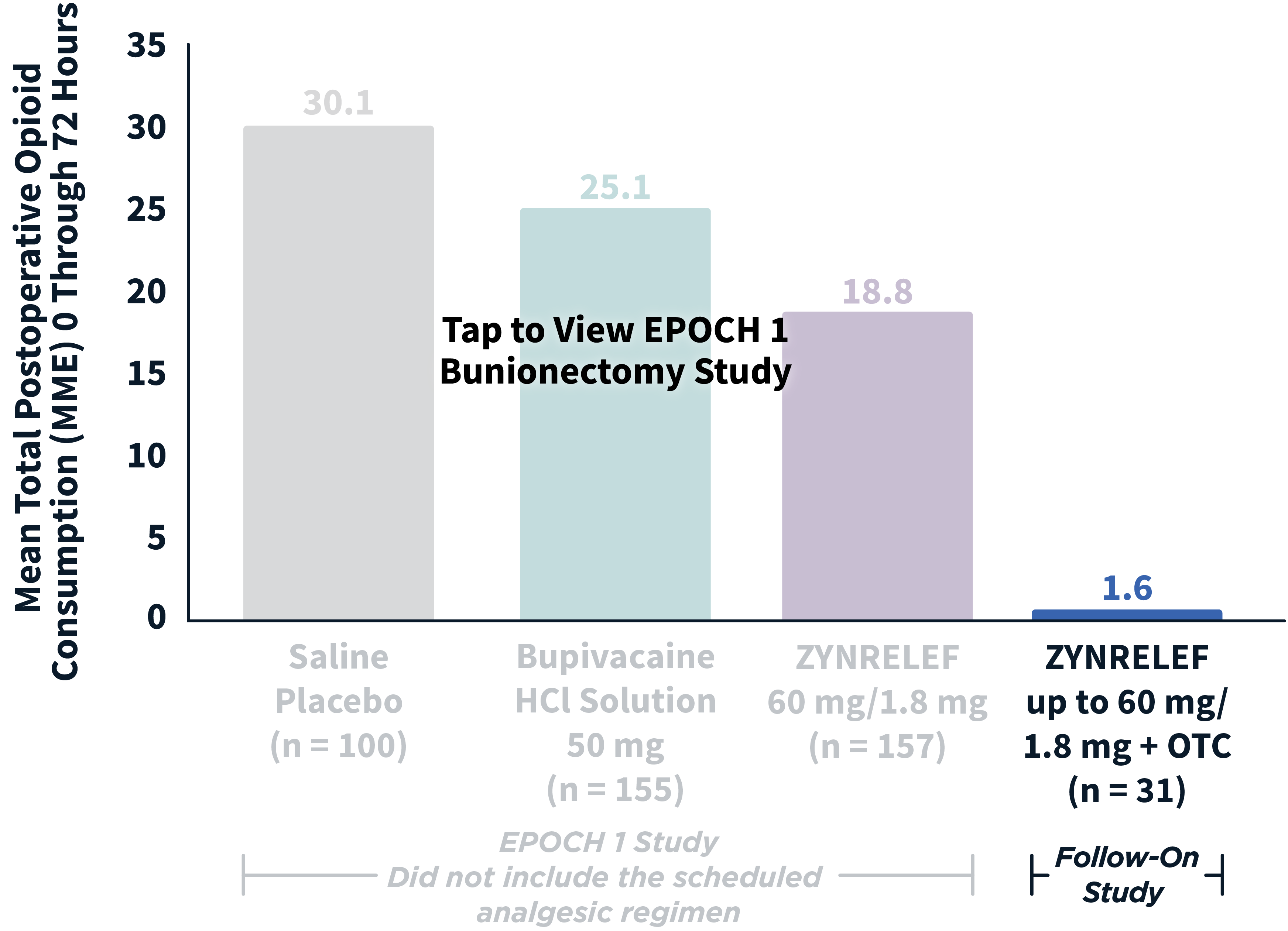
ZYNRELEF vs Placebo: P < .001
ZYNRELEF vs Bupivacaine HCl Solution: P = .002
MME: morphine milligram equivalents.
OTC: over-the-counter. EPOCH 1 Single-Arm Follow-On provided a non-opioid OTC regimen of oral ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
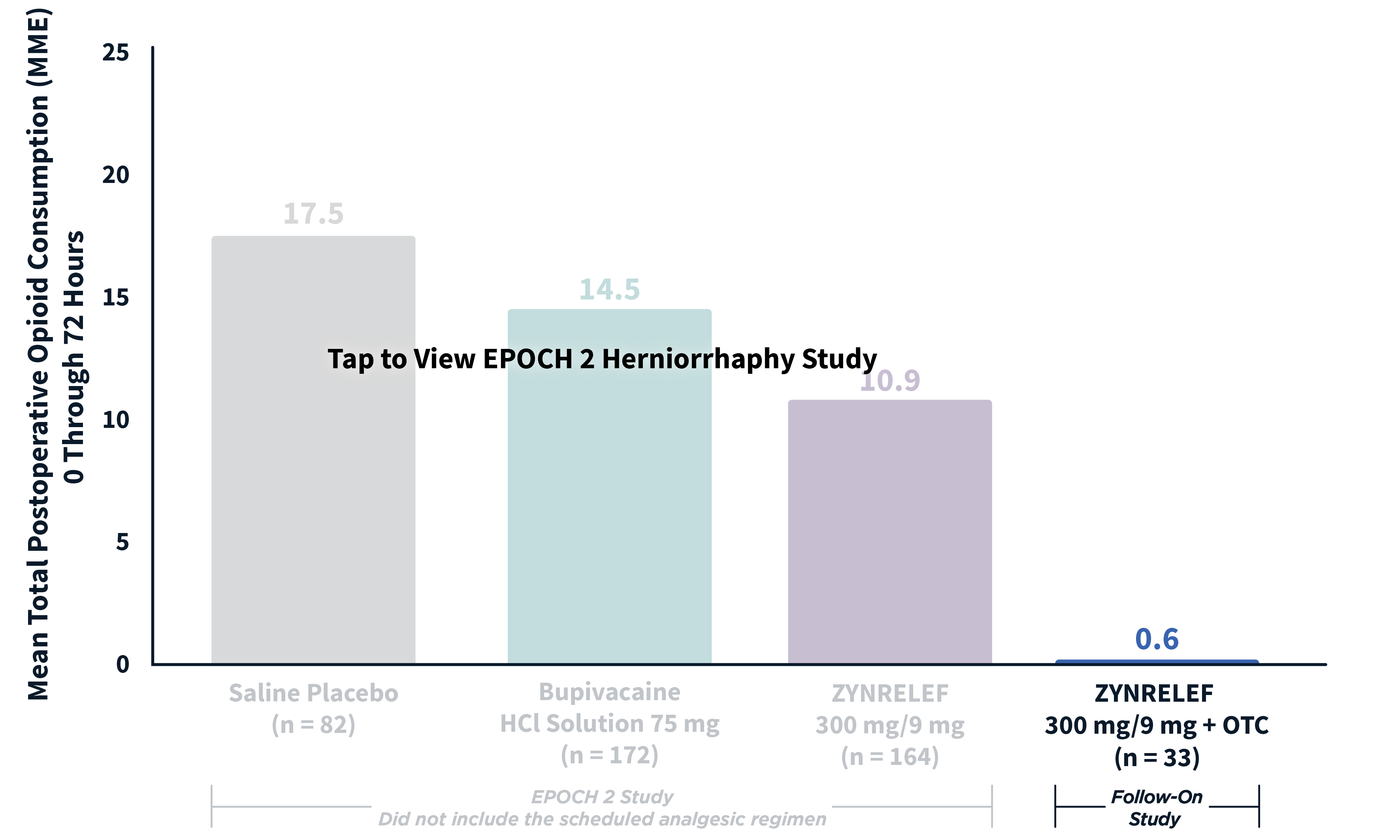
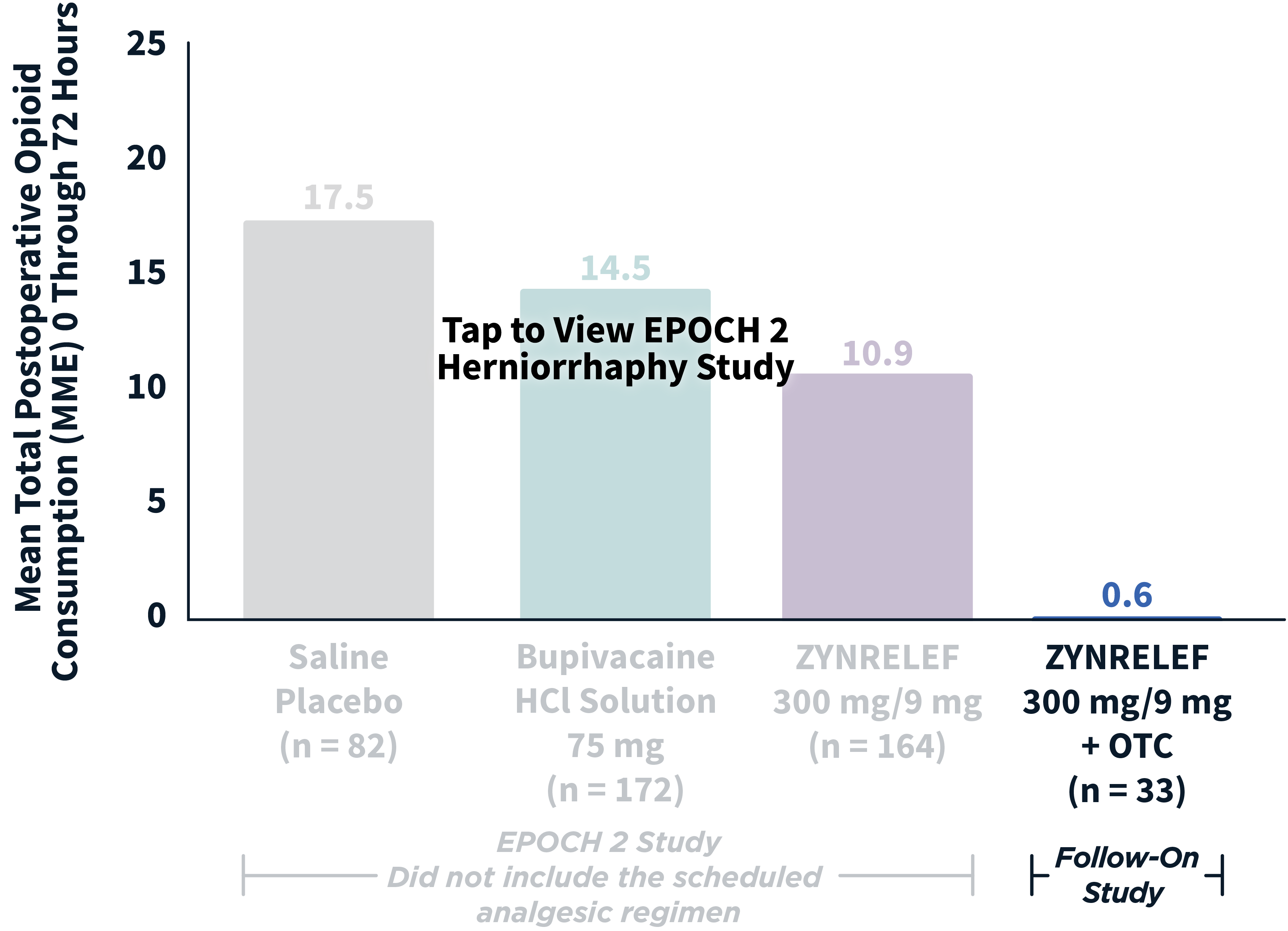
ZYNRELEF vs Placebo: P < .001
ZYNRELEF vs Bupivacaine HCl Solution: P = .02
MME: morphine milligram equivalents.
OTC: over-the-counter. EPOCH 2 Single-Arm Follow-On provided a non-opioid OTC regimen of oral ibuprofen and acetaminophen.
The mean consumption of opioids in the EPOCH TKA Single-Arm Follow-On study was 1 to 2 pills of oxycodone 10 mg per day through 72 hours (25 MME).
39% of TKA patients treated with ZYNRELEF and a non-opioid MMA regimen received no opioid discharge prescription and had no callbacks through day 11 of recovery
Severe Pain: pain intensity score of ≥7 on a Numeric Rating Scale of 0 to 10.
MME: morphine milligram equivalents.
MMA: multimodal analgesia.
ZYNRELEF is indicated in adults for instillation to produce postsurgical analgesia for up to 72 hours after soft tissue and orthopedic procedures including foot and ankle, and other procedures in which direct exposure to articular cartilage is avoided.
Limitations of Use: Safety and efficacy have not been established in highly vascular surgeries, such as intrathoracic, large 4 or more level spinal, and head and neck procedures.
ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity (eg, anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to any amide local anesthetic, NSAIDs, or other components of ZYNRELEF; with history of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients); undergoing obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia; or undergoing CABG.
Dose-Related Toxicity: Monitor cardiovascular and respiratory vital signs and patient’s state of consciousness after application of ZYNRELEF. When using ZYNRELEF with other local anesthetics, overall local anesthetic exposure must be considered through 72 hours.
Hepatotoxicity: If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medication may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure.
Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of ZYNRELEF in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure.
Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of ZYNRELEF in patients with advanced renal disease unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal failure.
Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
Risk of Joint Cartilage Necrosis and Degeneration with Unapproved Intra-articular Use: Animal studies evaluating the effects of ZYNRELEF following intra-articular administration in the knee joint demonstrated cartilage necrosis and degeneration.
Chondrolysis: Limit exposure to articular cartilage due to the potential risk of chondrolysis.
Methemoglobinemia: Cases have been reported with local anesthetic use.
Serious Skin Reactions: NSAIDs, including meloxicam, can cause serious skin adverse reactions. NSAIDs can also cause fixed drug eruption (FDE). FDE may present as a more severe variant known as generalized bullous fixed drug eruption (GBFDE), which can be life-threatening. If symptoms present, evaluate clinically.
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): If symptoms are present, evaluate clinically.
Fetal Toxicity: Due to the risk of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction and premature closure of the ductus arteriosus with NSAIDs, limit use of ZYNRELEF between about 20 to 30 weeks gestation, and avoid use after about 30 weeks.
Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia.
Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis: Monitor patients for bleeding who are using ZYNRELEF with drugs that interfere with hemostasis (eg, warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs).
ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs), or Beta-Blockers: Use with ZYNRELEF may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure.
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Use with ZYNRELEF in elderly, volume-depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high-risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function.
Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects.
Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider avoidance of ZYNRELEF in women who have difficulties conceiving.
Severe Hepatic Impairment: Only use if benefits are expected to outweigh risks; monitor for signs of worsening liver function.
Severe Renal Impairment: Not recommended.
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) in controlled clinical trials with ZYNRELEF are soft tissue procedures: vomiting and orthopedic procedures: constipation and headache.
Report side effects to Heron at 1-844-437-6611 or to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
ZYNRELEF is indicated in adults for instillation to produce postsurgical analgesia for up to 72 hours after soft tissue and orthopedic procedures including foot and ankle, and other procedures in which direct exposure to articular cartilage is avoided.
Limitations of Use: Safety and efficacy have not been established in highly vascular surgeries, such as intrathoracic, large 4 or more level spinal, and head and neck procedures.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning and updated Warnings and Precautions for serious skin reactions caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
How could you incorporate ZYNRELEF as the foundation of your institution’s postoperative pain management strategy? Connect with us to find out.
Fields marked with an asterisk (*) are required.
In the meantime, you can learn more about ZYNRELEF by viewing our Frequently Asked Questions or downloading our Resources.
844-HERON11 (844-437-6611)