Meet the first and only extended-release dual-acting local anesthetic
JUMP TO SECTION:
JUMP TO SECTION:
As the first and only extended-release dual-acting local anesthetic, ZYNRELEF is uniquely designed to address the challenges of inflammation at the surgical site and serve as a non-opioid foundation for postoperative pain management.1-5
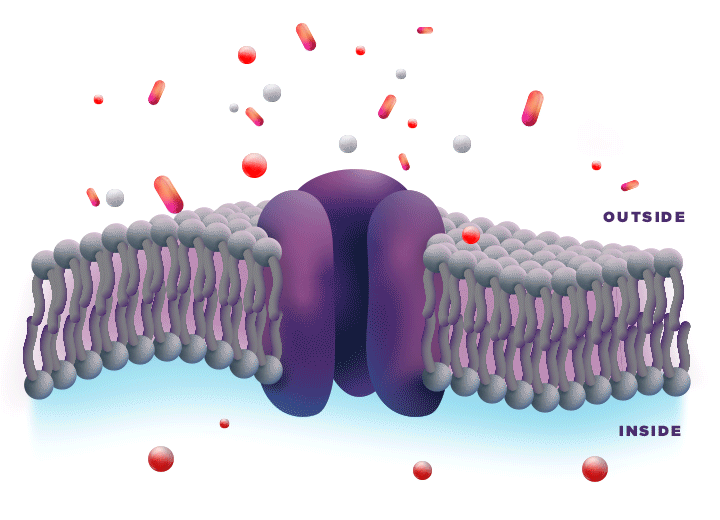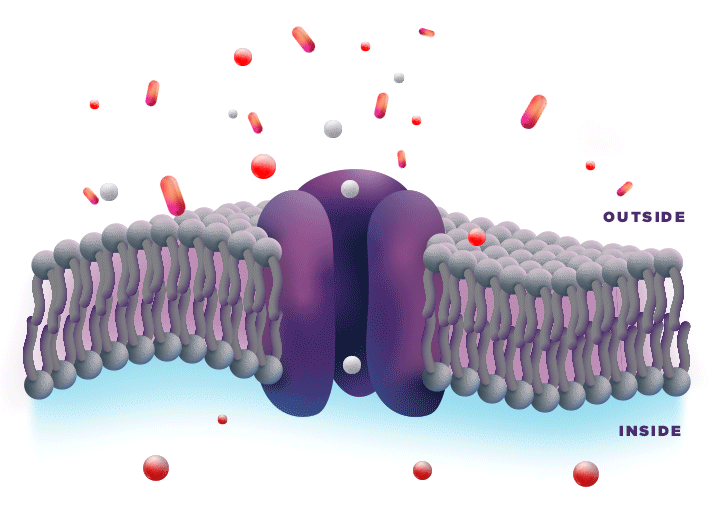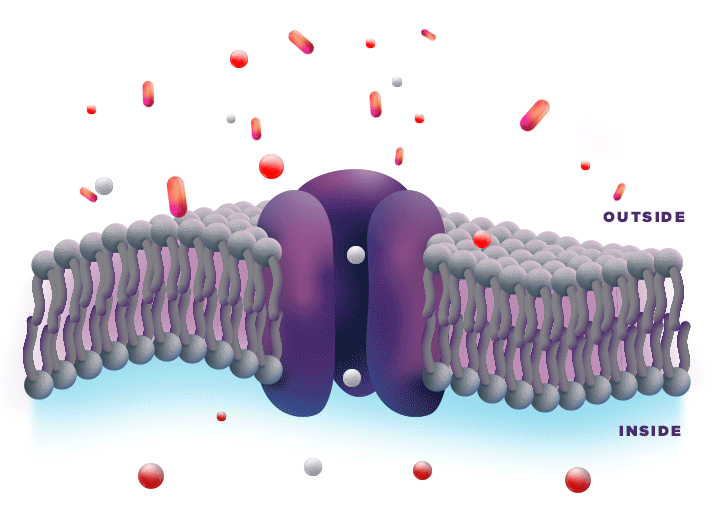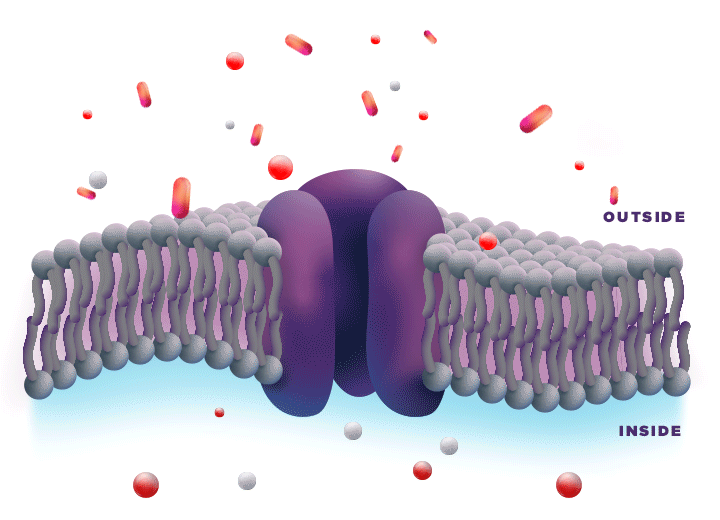
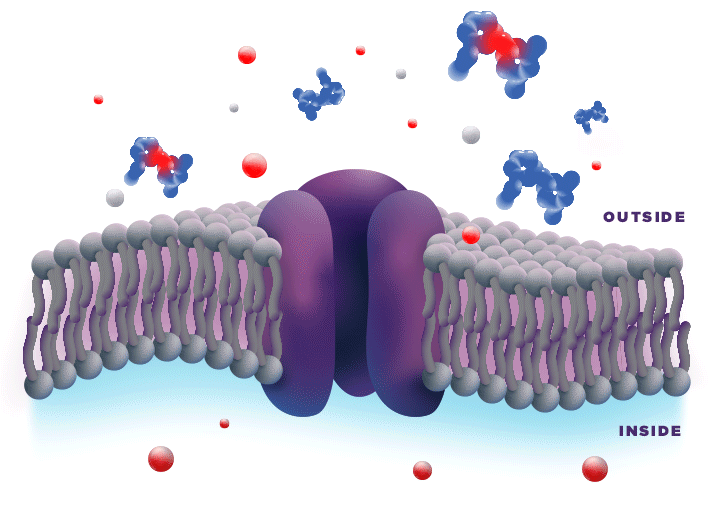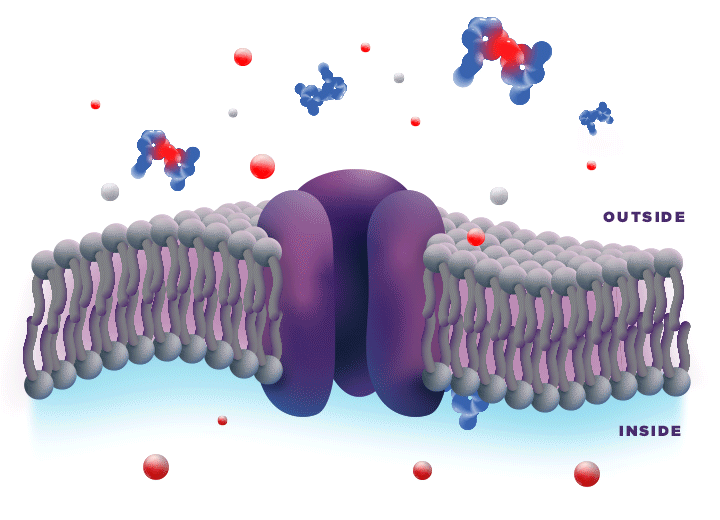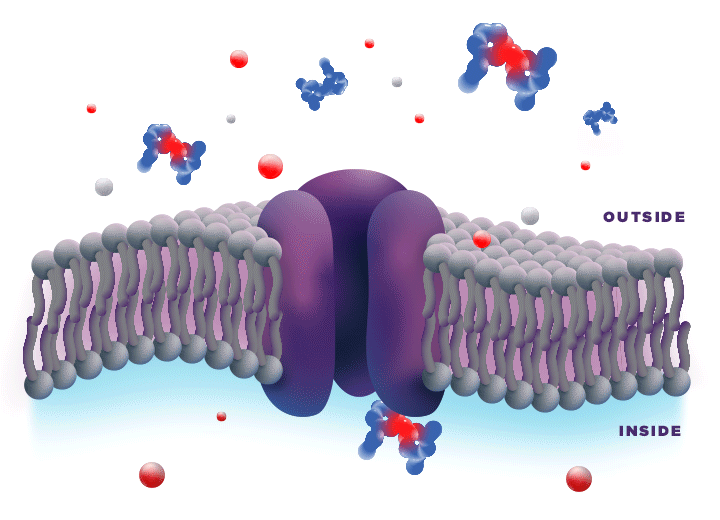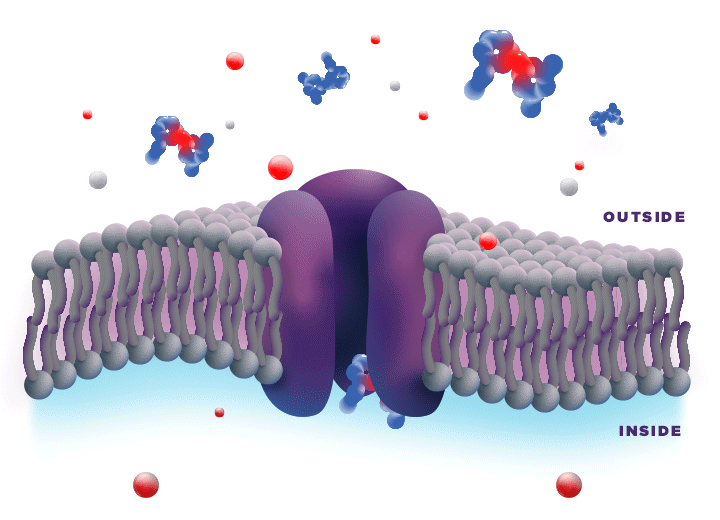
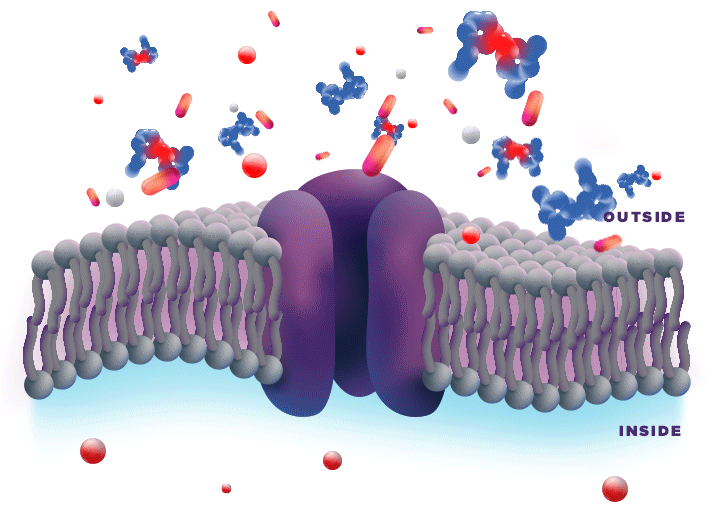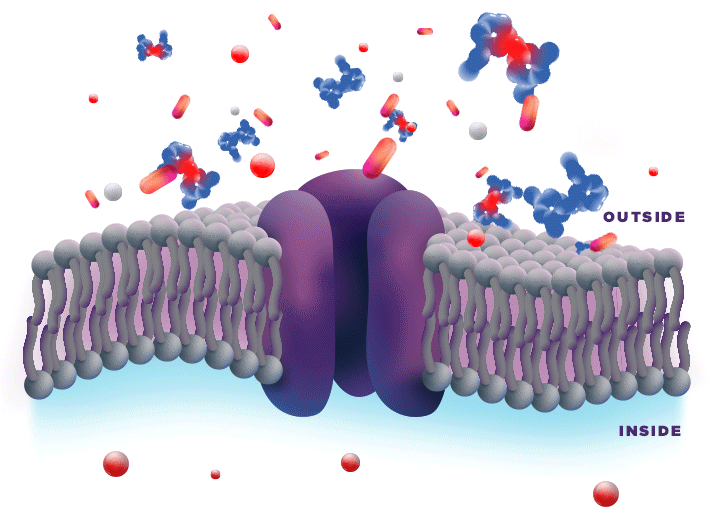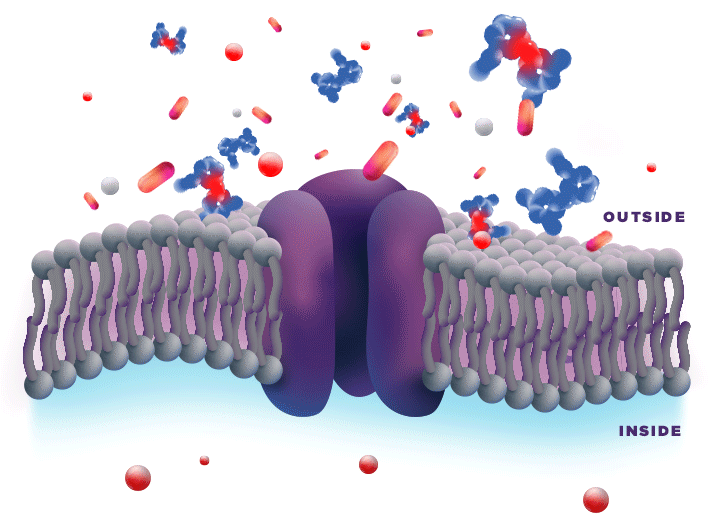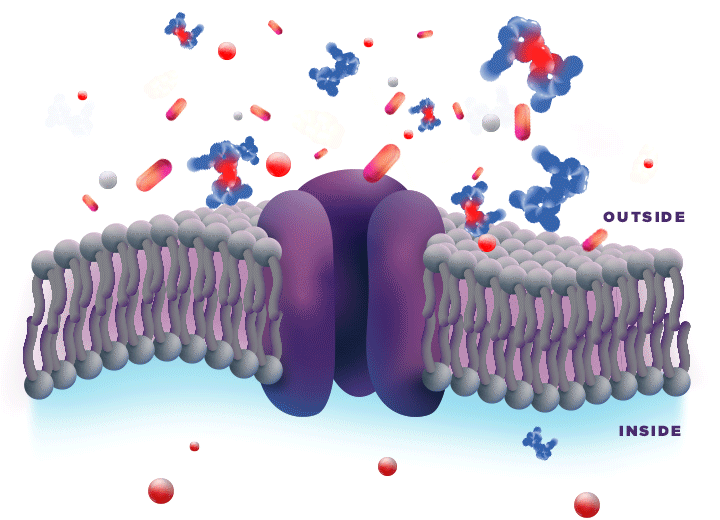
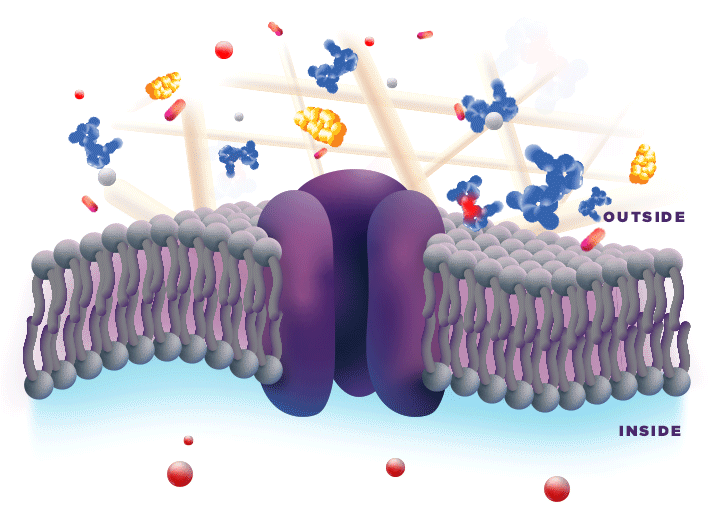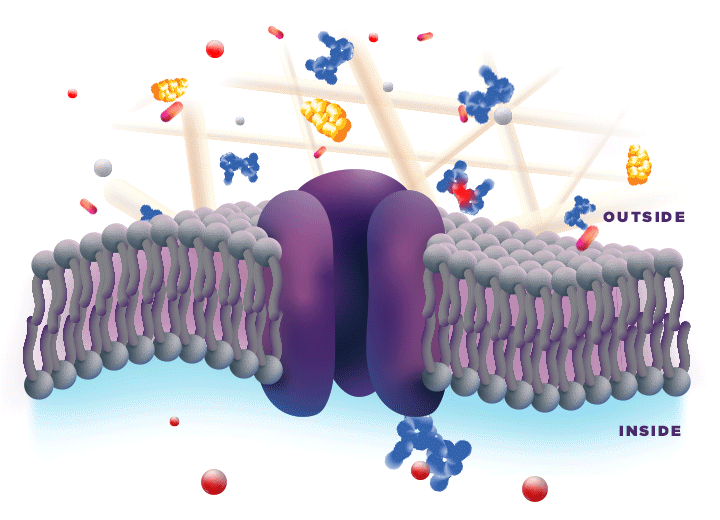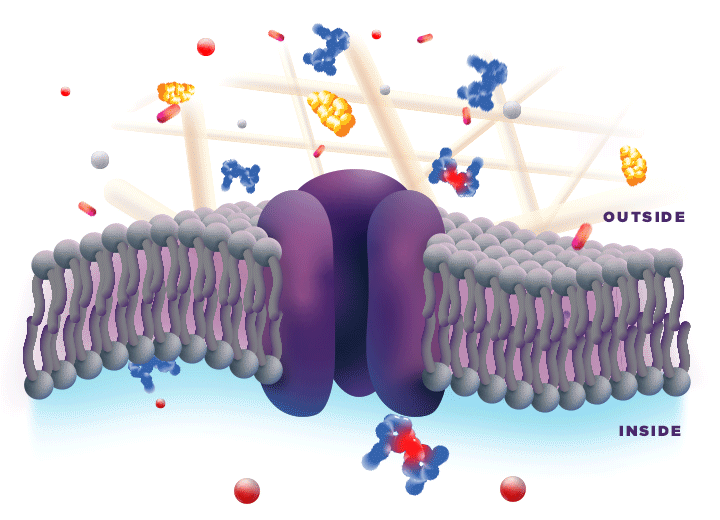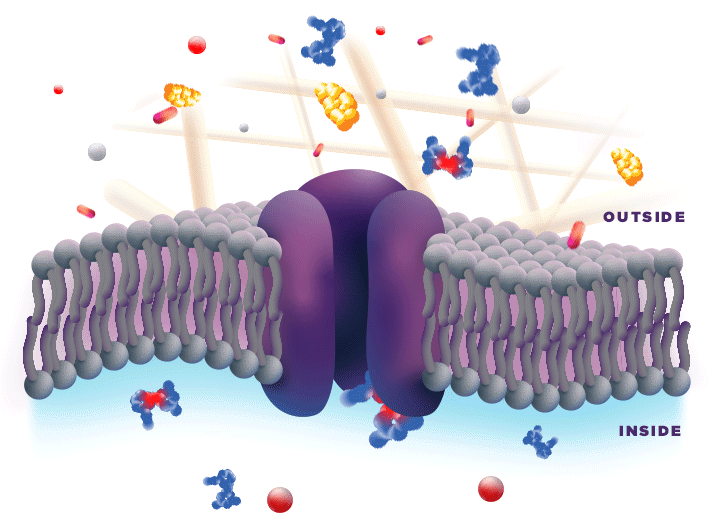
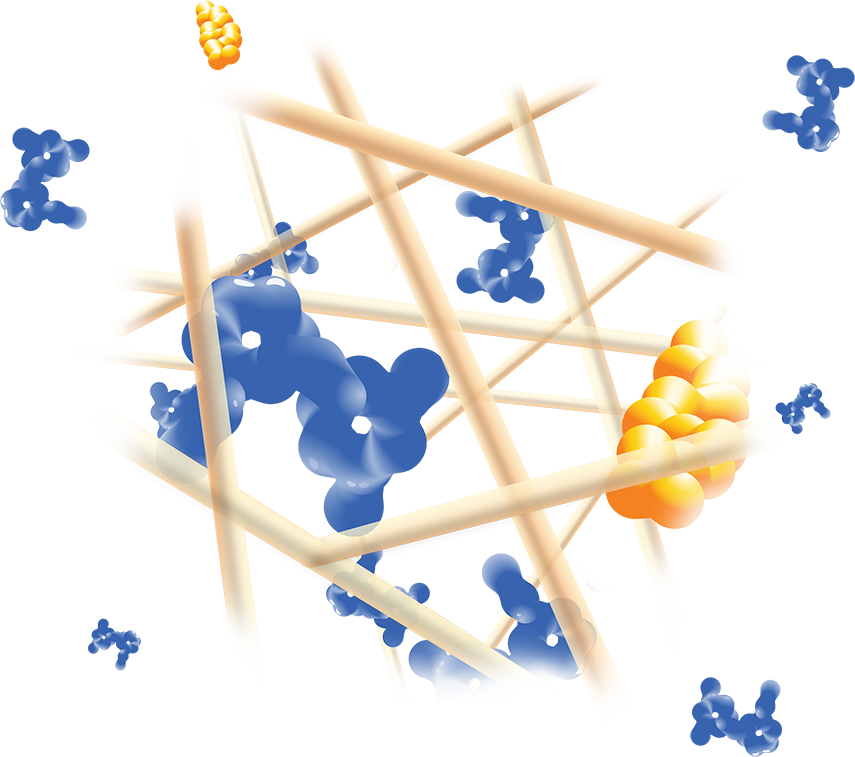
ZYNRELEF is delivered in a proprietary extended-release Biochronomer polymer that provides controlled diffusion of the active ingredients at the surgical site to enable sustained, consistently regulated delivery over the course of 72 hours.1,5
ZYNRELEF is a fixed-dose combination of bupivacaine and low-dose meloxicam. The ratio of bupivacaine to meloxicam is 33:1.1 As the active components are released from the formulation, the polymer hydrolyzes into benign, water-soluble end products, which are eliminated from the body.5
The Biochronomer polymer technology is in a product that has been used more than 300,000 timesa for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) patients; it has been applied in more than 50,000 ZYNRELEF patients.1,15-18,b
No mixing with bupivacaine is required to achieve efficacy with ZYNRELEF. The meloxicam in ZYNRELEF potentiates the effects of bupivacaine over 72 hours without needing support from additional products. It should be applied as is, without diluting or mixing with water, saline, or other local anesthetics. When ZYNRELEF comes in contact with moisture in the tissues, it becomes more viscous, allowing it to stay in place and deliver the active ingredients for the first 72 hours after surgery. Because no mixing with bupivacaine is required to achieve efficacy, there is no risk of calculation error.1
Due to the novel properties of the Biochronomer polymer, other local anesthetics can be administered before ZYNRELEF without causing release of the active ingredients all at once. The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Avoid additional use of local anesthetics within 96 hours following administration of ZYNRELEF.1
aBased on units distributed.
bCombined prescription and clinical trial data.
CINV: chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
Registering will put you at the front of the line to receive updates on the availability of ZYNRELEF and tools and resources.
ZYNRELEF is indicated in adults for instillation to produce postsurgical analgesia for up to 72 hours after soft tissue and orthopedic procedures including foot and ankle, and other procedures in which direct exposure to articular cartilage is avoided.
Limitations of Use: Safety and efficacy have not been established in highly vascular surgeries, such as intrathoracic, large 4 or more level spinal, and head and neck procedures.
ZYNRELEF is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity (eg, anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to any amide local anesthetic, NSAIDs, or other components of ZYNRELEF; with history of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients); undergoing obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia; or undergoing CABG.
Dose-Related Toxicity: Monitor cardiovascular and respiratory vital signs and patient’s state of consciousness after application of ZYNRELEF. When using ZYNRELEF with other local anesthetics, overall local anesthetic exposure must be considered through 72 hours.
Hepatotoxicity: If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medication may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure.
Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of ZYNRELEF in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure.
Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of ZYNRELEF in patients with advanced renal disease unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal failure.
Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
Risk of Joint Cartilage Necrosis and Degeneration with Unapproved Intra-articular Use: Animal studies evaluating the effects of ZYNRELEF following intra-articular administration in the knee joint demonstrated cartilage necrosis and degeneration.
Chondrolysis: Limit exposure to articular cartilage due to the potential risk of chondrolysis.
Methemoglobinemia: Cases have been reported with local anesthetic use.
Serious Skin Reactions: NSAIDs, including meloxicam, can cause serious skin adverse reactions. NSAIDs can also cause fixed drug eruption (FDE). FDE may present as a more severe variant known as generalized bullous fixed drug eruption (GBFDE), which can be life-threatening. If symptoms present, evaluate clinically.
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): If symptoms are present, evaluate clinically.
Fetal Toxicity: Due to the risk of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction and premature closure of the ductus arteriosus with NSAIDs, limit use of ZYNRELEF between about 20 to 30 weeks gestation, and avoid use after about 30 weeks.
Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia.
Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis: Monitor patients for bleeding who are using ZYNRELEF with drugs that interfere with hemostasis (eg, warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs).
ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs), or Beta-Blockers: Use with ZYNRELEF may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure.
ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Use with ZYNRELEF in elderly, volume-depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high-risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function.
Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects.
Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider avoidance of ZYNRELEF in women who have difficulties conceiving.
Severe Hepatic Impairment: Only use if benefits are expected to outweigh risks; monitor for signs of worsening liver function.
Severe Renal Impairment: Not recommended.
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) in controlled clinical trials with ZYNRELEF are soft tissue procedures: vomiting and orthopedic procedures: constipation and headache.
Report side effects to Heron at 1-844-437-6611 or to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
ZYNRELEF is indicated in adults for instillation to produce postsurgical analgesia for up to 72 hours after soft tissue and orthopedic procedures including foot and ankle, and other procedures in which direct exposure to articular cartilage is avoided.
Limitations of Use: Safety and efficacy have not been established in highly vascular surgeries, such as intrathoracic, large 4 or more level spinal, and head and neck procedures.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning and updated Warnings and Precautions for serious skin reactions caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
How could you incorporate ZYNRELEF as the foundation of your institution’s postoperative pain management strategy? Connect with us to find out.
Fields marked with an asterisk (*) are required.
In the meantime, you can learn more about ZYNRELEF by viewing our Frequently Asked Questions or downloading our Resources.
844-HERON11 (844-437-6611)